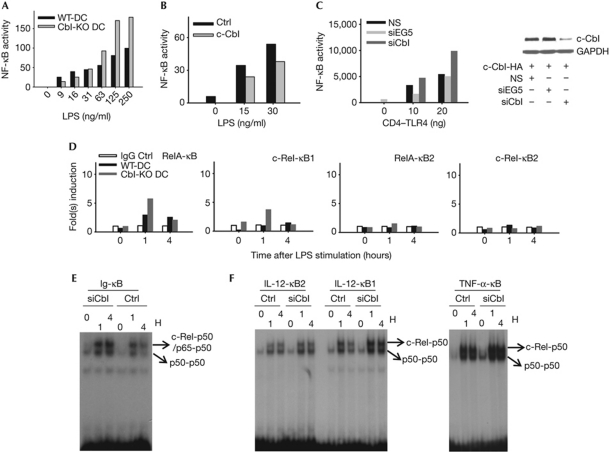
Figure 4.
c-Cbl inhibits the expression of proinflammatory cytokines by attenuating the recruitment of stimulatory NF-κB heterodimers. (A) WT and Cbl-KO BMDCs were nucleofected with normalized amounts of NF-κB-SEAP reporter and incubated for 8–10 h. Subsequently, cells were stimulated with titrated LPS overnight. Supernatants were collected and prepared for SEAP assay. (B) Cbl-KO BMDCs were nucleofected with NF-κB-SEAP reporter plus either control vector or WT c-Cbl construct before stimulation with titrated LPS before SEAP assay, as described in (A). (C) 293T cells were transduced with the indicated lentivirus (pGIPZ, NS) and the transductants were selected for the GFP+ population in the presence of puromycin (5 μg/ml). After 2 weeks, normalized numbers of transductants were seeded onto a 12-well plate before transfection with the WT c-Cbl and CD4–TLR4 constructs. Supernatants were collected and prepared for SEAP assay, as described in (A,B). On collection of supernatants, cells were prepared for western blot analysis (right panel). (D) Paired WT and Cbl-KO BMDCs were stimulated with LPS at the indicated time points before fixation for chromatin immunoprecipitation. A previously reported NF-κB site located at the distal end of the murine IL-12p35 promoter was used as negative control (κB2). The proximal NF-κB site derived from the same promoter (κB1) was examined for specific binding of the indicated NF-κB family members. (E,F) Nuclear lysates were prepared and electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed by using the indicated probes. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments with consistent results. Cbl-KO, c-Cbl-knockout; DC, dendritic cell; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HA, haemagglutinin; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NS, non-silencing; siRNA, small-interfering RNA; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumour-necrosis factor; WT, wild type.