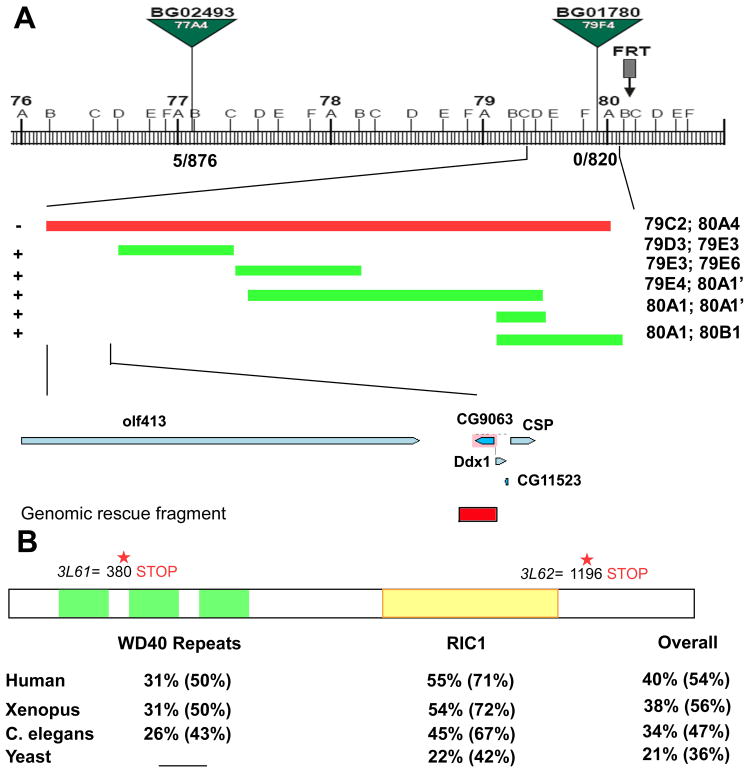
Figure 3. 3L6 encodes an evolutionarily conserved gene CG9063 (rich).
(A) Schematic showing the cytological interval and the position of the P-elements and the overlapping deficiencies used to identify the genomic region of the 3L6. The recombination rate is 5/876 for BG02493 and 0/820 for BG01780. “−” indicates “fail to complement” and “+” indicates “complements” 3L61 and 2. The lower panel shows genes in the region identified by deficiency mapping and the genomic rescue fragment of rich (Red box). (B) Schematic of the Rich protein showing the predicted domains and the locations of the stop codons in 3L61 and 3L62. The bottom panel shows the homology (identity %; similarity %) of WD40 repeats domain, RIC1 domain, and overall protein sequence between Rich and its homologs in humans, frogs, worms, and yeast.