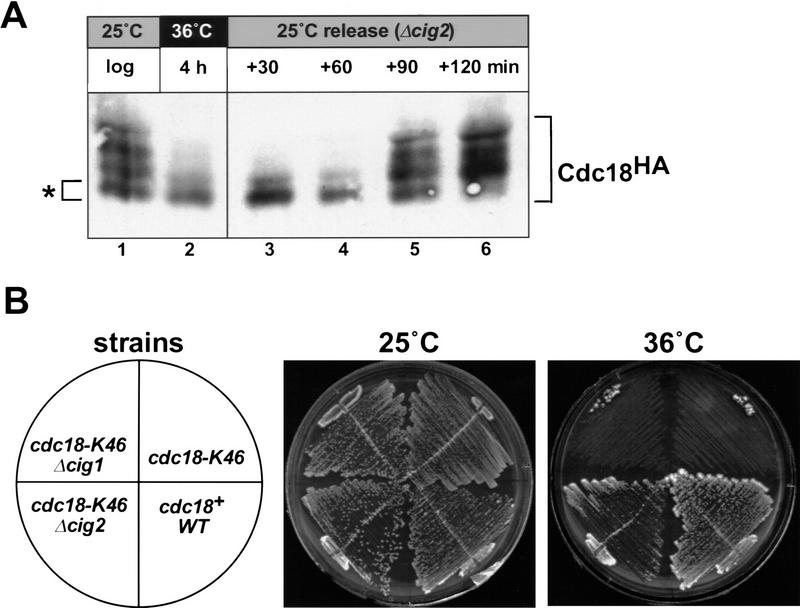
Figure 3.
S-phase CDK activity promotes phosphorylation of p65cdc18 and antagonizes its function in vivo. (A) Deletion of the S-phase cyclin cig2+ delays the onset of p65cdc18 modification. The G1 synchronization protocol used in Fig. 2 was performed with a similar cdc10–V50 strain also harboring a deletion of the S-phase cyclin cig2+. Note that the appearance of slower migrating forms of p65cdc18 is delayed in Δcig2 cells by ∼30 min (cf. Fig. 2A). (B) Deletion of cig2+ suppresses the cell cycle defect of a temperature-sensitive cdc18 mutation. Fission yeast strains with the indicated genotypes were constructed by standard genetic methods and tested for viability at 25°C (permissive temperature for cdc18–K46) or 36°C (restrictive temperature).