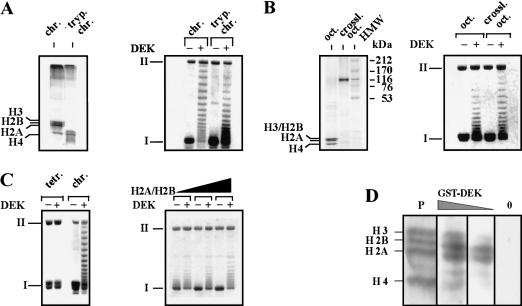
Figure 4.
The DEK-induced change in topology depends on the presence of H2A/H2B dimers. (A, left) The amino-terminal histone domains of SV40 minichromosomes were removed by trypsin. Polypeptides were investigated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. (Right) Non-treated chromatin (chr.) and trypsinized chromatin (tryp. chrom.) was used as substrate in the DEK assay. (B, left) Histone octamers (oct.) were cross-linked with DMS (crossl. oct.) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (HMW) High molecular weight marker in kilodaltons. (Right) SV40 DNA was reconstituted with control or cross-linked octamers and used as substrate in the DEK assay. (C, left) SV40 DNA was reconstituted with purified H3/H4 tetramers (tetr.) or histone octamers (chrom.). Chromatin was incubated in the absence or presence of DEK. (Right) H3/H4 containing chromatin was reconstituted with increasing amounts of H2A/H2B dimers and used as substrate in the DEK assay. (D) Far-Western blot analysis. Core histones were separated on an SDS–polyacrylamide gel, electroblotted, and renatured. The membrane was stained with Ponceau red (P) and incubated with decreasing amounts of GST–DEK (100 ng/cm2; 25 ng/cm2) and without DEK (0). The position of the core histones are indicated.