Figure 7.
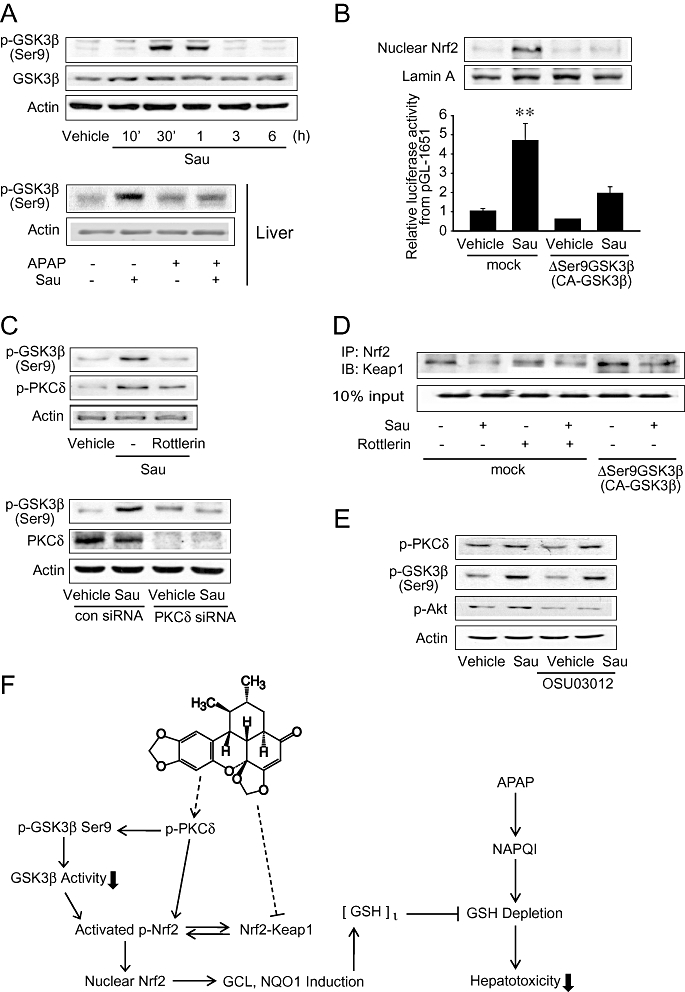
Increase in GSK3β phosphorylation by sauchinone (Sau). (A) Immunoblottings for glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β). Ser9-phosphorylated or total GSK3β was immunochemically measured on the lysates of HepG2 cells treated with 30 µM Sau for 10 min–6 h (upper), or on the homogenates of livers of mice treated with 30 mg·kg−1 Sau and/or 500 mg·kg−1 acetaminophen (APAP) for 6 h (lower). Results were confirmed in three separate experiments. (B) Reversal by ΔSer9GSK3β (CA-GSK3β) of the ability of Sau to activate nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2 (Nrf2). Nrf2 was immunoblotted in the lysates of mock- or ΔSer9GSK3β-transfected cells treated with vehicle or Sau for 3 h. Lamin A immunoblotting verified equal loading and the purity of nuclear proteins (upper). Luciferase activity was measured on the lysates of cells that had been transfected with pGL-1651 in combination with ΔSer9GSK3β for 24 h, followed by Sau treatment (lower). (C) Inhibition of Sau-induced GSK3β phosphorylation by protein kinase C δ (PKCδ) inhibition. The proteins of interest were immunoblotted on the lysates of cells treated with vehicle, Sau, Sau + rottlerin for 1 h. Similarly, the proteins were assessed after transfection with non-targeting siRNA (con siRNA) or siRNA directed against PKCδ. Results were confirmed by three repeated experiments. (D) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot assays. Interaction between Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1) and Nrf2 was measured in mock- or CA-GSK3β-transfected HepG2 cells that had been treated with 5 µM rottlerin for 1 h and continuously exposed to vehicle or Sau for 3 h. Nrf2 immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblottings for Keap1. Results were confirmed by repeated experiments. (E) Immunoblottings for p-PKCδ or p-GSK3β (Ser9) on the lysates of cells treated with 1 µM OSU03012 for 1 h and continuously incubated with Sau for 1 h. (F) A schematic diagram illustrating the proposed mechanism by which sauchinone protects the liver against APAP-induced toxicity. GCL, glutamate-cysteine ligase; GSH, glutathione; NAPQI, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine; NQO1, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase-1.
