Figure 1.
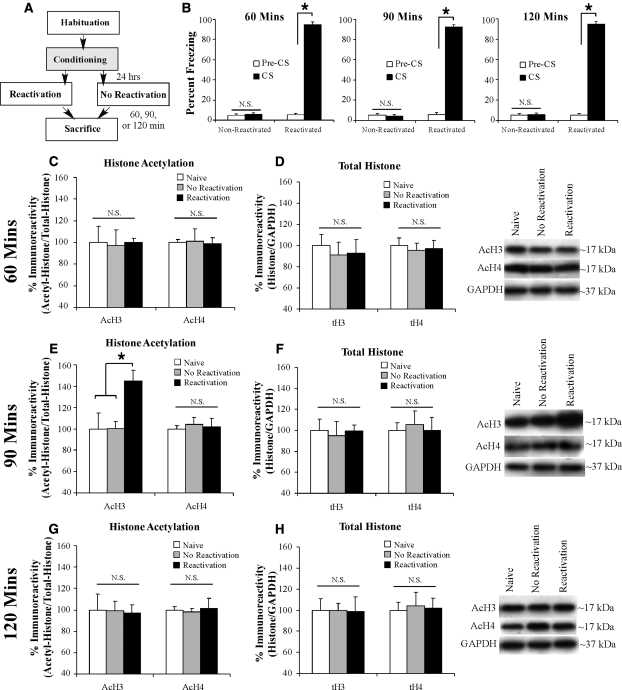
Auditory fear memory retrieval transiently regulates histone H3 acetylation in the LA. (A) Schematic of the behavioral protocol. Rats were handled and habituated to both the training and testing context for 4 d prior to fear conditioning. Twenty-four hours following training, rats were given either a reactivation or no-reactivation session and were sacrificed 60, 90, or 120 min later. (B) Memory retrieval data for the 60-, 90-, and 120-min groups during the no-reactivation and reactivation trials. *P < 0.05 relative to the preCS period. (C) Western blot analysis of acetylated histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 7), and reactivated rats (n = 7) sacrificed 60 min after reactivation session. (D) Western blot analysis of total histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 7), and reactivated rats (n = 7) sacrificed 60 min after reactivation session. (E) Western blot analysis of acetylated histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 6), and reactivated (n = 9) rats sacrificed 90 min after reactivation session. *P < 0.05 relative to nonreactivated and naive groups. (F) Western blot analysis of total histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 6), and reactivated (n = 9) rats sacrificed 90 min after reactivation session. (G) Western blot analysis of acetylated histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 7), and reactivated (n = 6) rats sacrificed 120 min after reactivation session. (H) Western blot analysis of total histone H3 and H4 from LA homogenates from naive (n = 8), nonreactivated (n = 7), and reactivated (n = 6) rats sacrificed 120 min after reactivation session. For each time point, representative Western blots are depicted in the inset.