Figure 4.
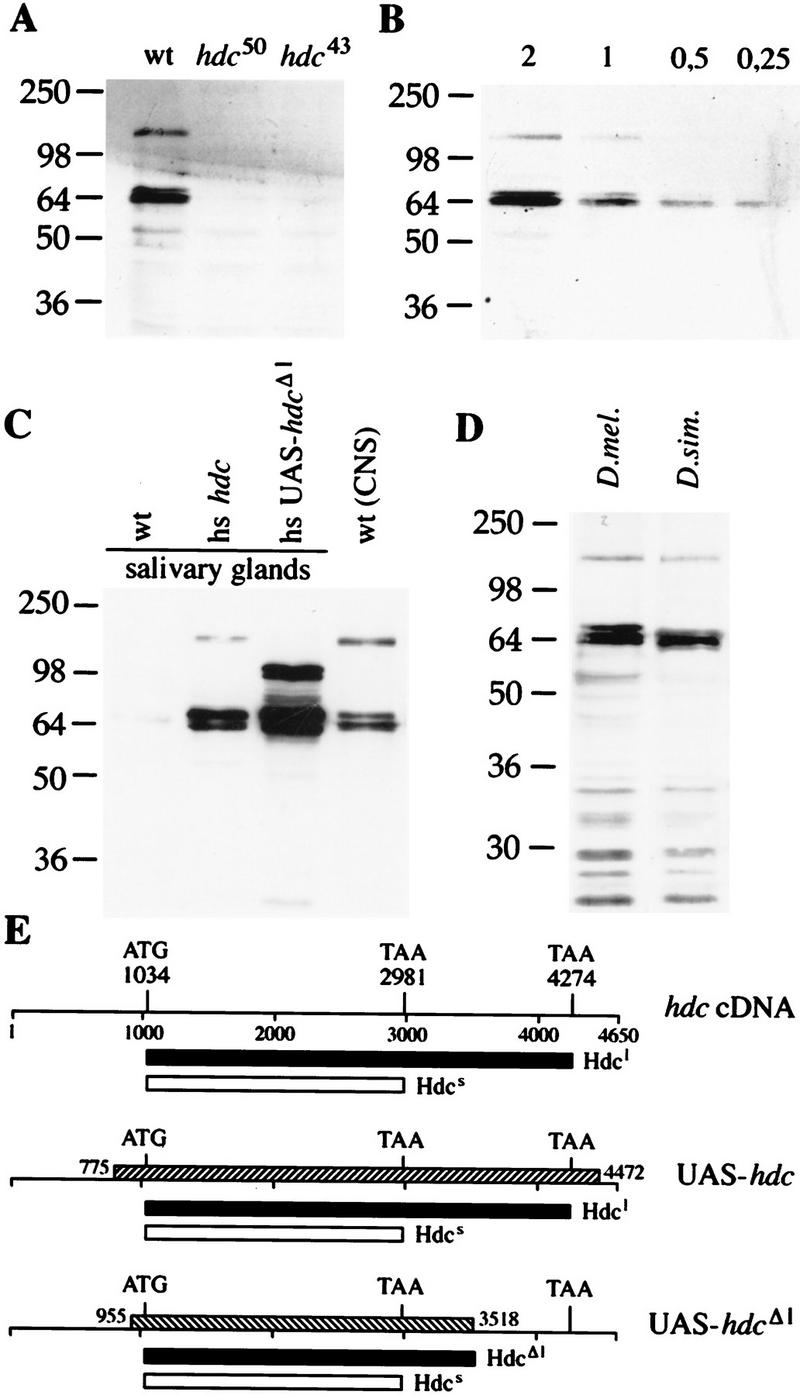
Translational readthrough generates two hdc products. Western blots probed with the antibody against the hdc products (A). The antibody recognizes two proteins in CNS and imaginal disk extracts from wild-type larvae. Both bands are absent in extracts from larvae homozygous for hdc50 and hdc43. (B) Quantitation of the amount of the two products relative to each other. Serial dilutions of a CNS and imaginal disk extract were loaded. The shorter product is ∼fourfold more abundant than the longer one. (C) Full-length cDNA is necessary to generate a product with the same size as the longer endogenous protein. Extracts of salivary glands from transgenic larvae carrying the full-length or a truncated version of the hdc cDNA under heat shock control were compared with CNS and imaginal disk extracts from wild type. (D) Two Hdc proteins are detected in extracts from D. simulans larval CNS and disks. (E) Drawings of the hdc cDNA clone and the fragments used to generate the transgenic strains shown as hatched bars. Start and stop codons are indicated and the predicted products are shown as black or white bars under each construct. Hdcl designates the longer product, and Hdcs the shorter one.
