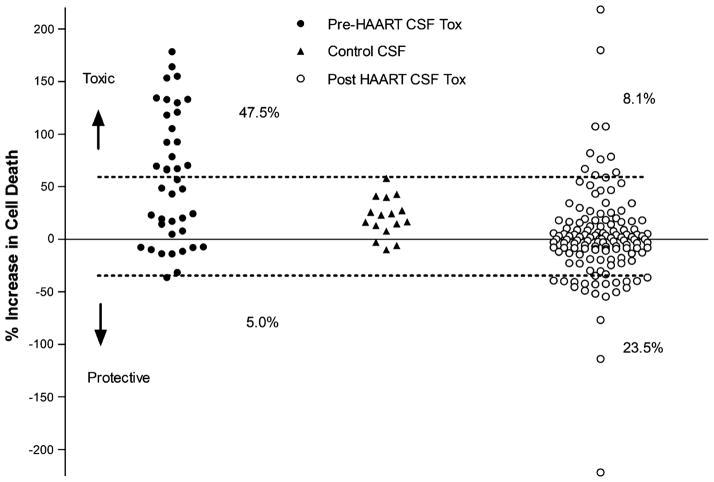
Fig. 1.
Summary of toxic activity in human CSF collected prior to (pre) or after (post) the introduction of HAART. Toxic activity was assessed by measuring relative changes in cell death (percent increase in cell death) in rat neural cultures treated with a 1:10 dilution of the CSF in culture medium as compared to cultures treated with artificial CSF. All stages of disease were represented in the samples. HIV-negative control CSF was used to define the normal range of CSF for comparison which was defined as the mean toxicity ±1.96 SD units (p<0.05, dashed lines). Data points falling above this range were counted as toxic and represented 47.5% of all pre-HAART CSF samples (n=40). Two values in the pre-HAART group fell below this range which was expected by chance. Of the 136 CSF samples analyzed after the introduction of HAART, 8.1% were toxic and 23.5% were below the cutoff, suggesting protective activity