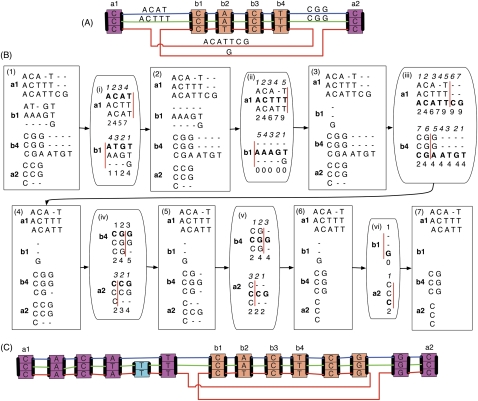
Figure 4.
An illustration of the BAR algorithm. (A) A subgraph of an adjacency subgraph. The magenta and orange coloring of the blocks highlights the two chains; the outer A chain contains the inner B chain, which has been inverted in the red thread. (B) An example of the BAR algorithm. Box (1), four end alignments are constructed, one for each end in the net that contains ends of A and B. The alignments are oriented from their respective ends. These four alignments are inconsistent; if they were accepted as they are, they would together create many likely spurious alignments. Box (i), the blue adjacency sequence ACAT between a1 and b1, is chosen at random. A cut point is chosen (drawn as a red line) on an induced alignment, one containing only the columns with residues in the chosen adjacency sequence. The cut point must lie before the first, after the last, or between two residues in the adjacency sequence. The cumulative alignment score of aligned pairs to the adjacency sequence is shown below the two induced alignments, in both cases cumulated away from the respective block end. The cut point is chosen so that the cumulated score before the cut point in the induced alignment of a1 plus the cumulated score after the cut point in the induced alignment of b1 is maximal. Alignments to the adjacency sequence in the a1 end alignment after the cut points are removed, and alignments to the adjacency sequence in the b1 alignment before the cut points are removed. In this case, the cut point is after position 4, so all of the a1 alignments are kept and all of the alignments to the adjacency sequence in the b1 alignment are removed. Box (2), the result of removing the alignments discarded in (i). Boxes (ii–vi) and (3–7) show this process repeated for each of the remaining adjacency sequences in turn. The ordering of adjacency sequences in this process is random. (C) The resulting adjacency subgraph after the alignments in Box (7) of B are included. The adjacency sequences are now all empty, and there are three chains, the orange and magenta chains, which have been lengthened, and a single block cyan chain corresponding to an indel.