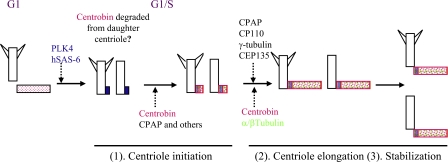
Figure 9.
Model of centrobin function during the centriole duplication process. The model summarizes our finding on the function of centrobin during centriole duplication. As the cell transitions from G1 to S phase, PLK4 activation leads to the recruitment of hSAS-6. Centrobin and other centriole initiation proteins are then recruited followed by centrobin, CPAP, CP110, γ-tubulin, and CEP135-mediated elongation of the centriole. Centrobin is also required to maintain the stability of the newly assembled centrioles before their maturation. Centrobin is likely degraded or displaced from the original daughter centriole once the centriole duplication starts.