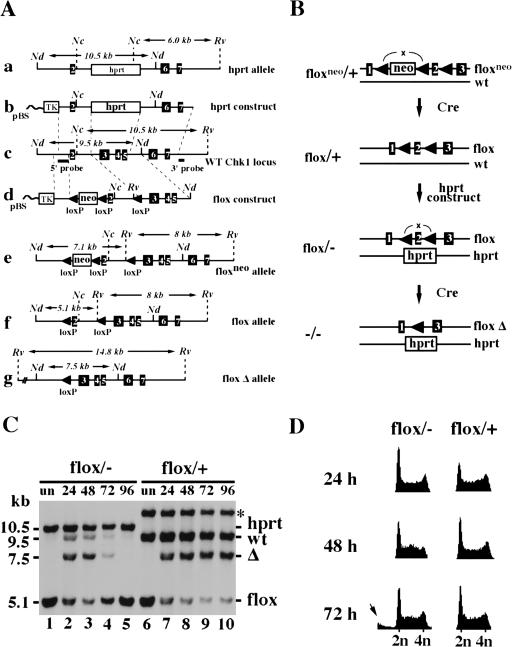
Figure 3.
Construction and analysis of a conditional CHK1-deficient ES cell line. (A) Restriction maps of targeting vectors and targeted alleles. (a) hprt targeted allele; (b) hprt targeting vector; (c) wild-type CHK1 locus; (d) flox targeting vector; (e) floxneo-targeted allele; (f) flox allele generated after neo excision; (g) flox Δ allele generated after excision of exon 2. Only relevant restriction sites are shown. (Nc) NcoI; (Nd) NdeI; (Rv) EcoRV. (B) A schematic representation of the construction of conditional CHK1-deficient ES cells. In brief, a CHK1 floxneo/+ cell line was first obtained using the flox-targeting vector followed by the Cre–loxP-mediated neo excision to create CHK1flox/+ cells. The remaining wild-type gene was then disrupted in the CHK1flox/+ cells by the hprt targeting vector to generate CHK1flox/− cells. Finally, CHK1flox/− cells were conditionally converted into CHK1−/− cells by excision of exon 2 by transient transfection of PGK:Cre. (C) A Southern blot showing excision of the flox allele in CHK1flox/+ and CHK1flox/− cells. Both are sister cell lines obtained from the same screen for generating CHK1flox/− cells. The asterisk refers to a band produced by random integration of the hprt construct in the CHK1flox/+ cells. Genomic DNA was prepared from untransfected (lanes 1,6) or Cre-transfected cells (lanes 2–5 and 7–10) collected at 24, 48, 72, and 96 hr after electroporation, digested with NdeI and EcoRV and probed with the 5′ internal probe. Δ refers to the excised flox allele. The faint wild-type band present in lanes 2–4 was contributed by the feeder cells. (D) Comparison of Cre-transfected CHK1flox/+ and CHK1flox/− cells by FACS (DNA content) analysis. Cells were harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hr after electroporation and stained with propidium iodide (PI). The arrow indicates cells with less than 2N DNA content that were present in the 72-hr flox/− sample.