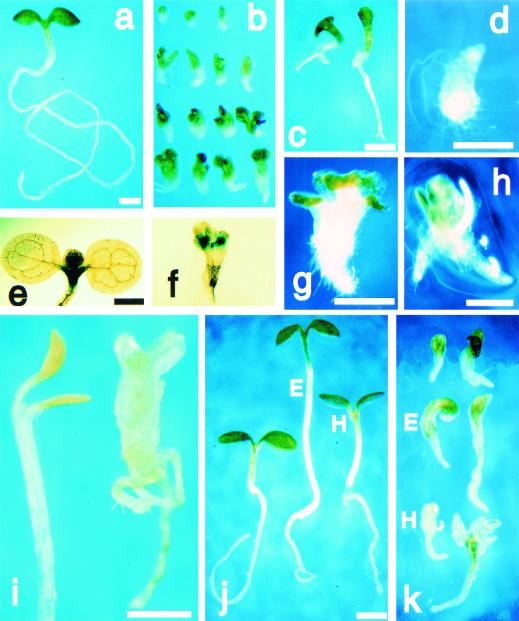
Figure 2.
fk seedling phenotype. (a–i) Seedlings were germinated on 1.7% agar/water for 11 days. (a,e) Wild type. (b–d,f–h) fk. (b) Phenotypic variability: The strong phenotypes (top) are severely stunted with a short root, malformed cotyledons, and appear to lack the hypocotyl. The weaker phenotypes (bottom) are larger; (c) weak allele fk-T329 shows longer root; (d) rooty seedling. KNAT2–GUS staining: (e) Wild type shows staining in shoot apical meristem; (f) fk shows multiple meristems; (g) seedling with multiple apices; (h) seedling with multiple roots; (i) etiolation response to germination in the dark: wild type (left) shows apical hook and elongation of the hypocotyl (one-third of the hypocotyl length is shown); fk (right) lacks apical hook and shows slightly elongated hypocotyl region; (j) wild-type control (left); treated with BRs 24-epibrassinolide (E, middle) or 22S,23S-homobrassinolide (H, right); (k) fk control (top); treatment with 24-epibrassinolide (E, center) or 22S,23S-homobrassinolide (H, bottom). Bars, 0.5 mm (a = b, e = f, g = h, j = k).