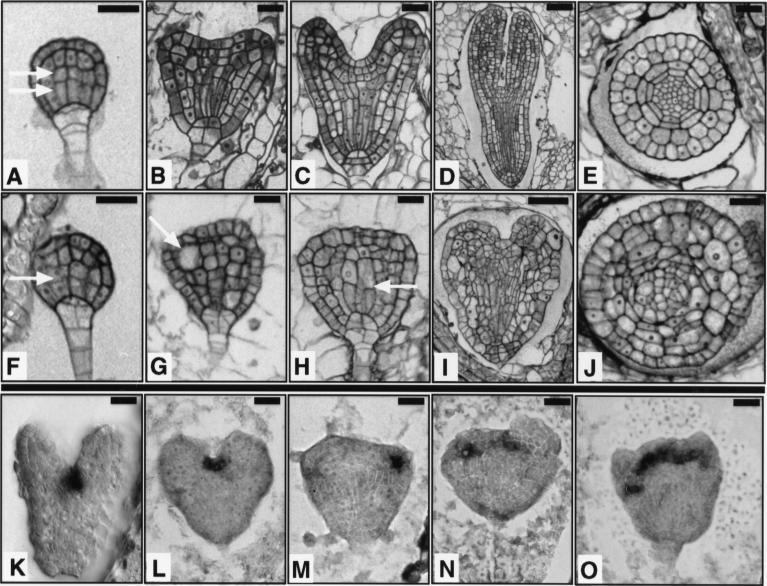
Figure 3.
Embryogenesis is abnormal in fk mutants. (A–E,K) Wild type. (F–J,L–O) fk. (A,F) Globular stage embryo. In wild type, the central vascular precursor cells divide asymmetrically to produce small apical and elongated basal cells (two arrows). In fk, the central cells divide to give cells of similar sizes (single arrow). (B,G) Early heart stage embryo. In wild type, the cotyledon primordia become visible and the central cells are elongated. In fk, cotyledon primordia are not visible and cells in the center of the embryo fail to elongate. Some cells are grossly enlarged (arrow); (C,H) Heart stage embryo. In wild type, the cotyledon primordia mark the bilateral symmetry of the embryo. fk embryos exhibit abnormal cell morphologies and incomplete cell walls (arrow); (D,I) Torpedo stage embryo. Wild-type embryo shows a characteristic torpedo shape. The fk embryo displays an abnormal heart shape and cell elongations leading to longitudinal outgrowth are defective. (E,J) Transverse sections of torpedo stage embryos. Wild-type embryo shows radial organization of tissue layers. The fk embryo lacks an organized radial pattern. Cells are misshapen and either larger or smaller than cells of the corresponding layer in wild type. (K–O) Heart stage embryos showing expression of STM mRNA, a shoot apical meristem marker. Wild-type expression is in the center, between the cotyledon primordia. fk embryos often show aberrant placement, multiple, or widened meristems. Bars, 20 μm (A–C,E–H,J); 40 μm (D,I).