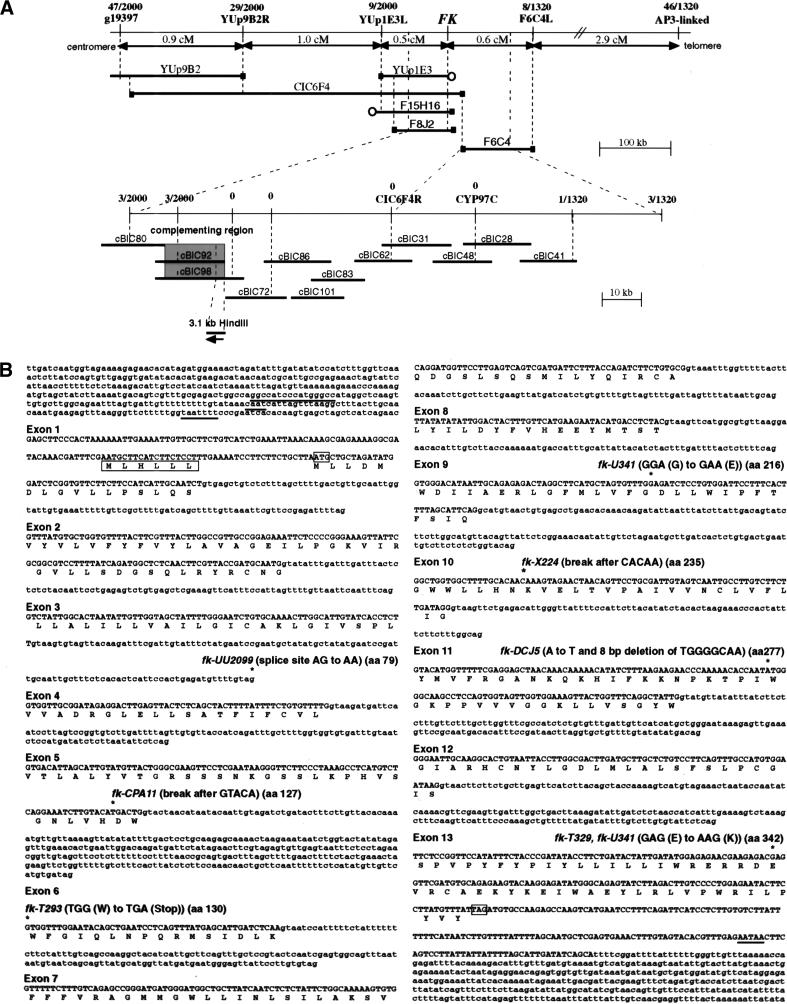
Figure 4.
Molecular identification of the FK gene. (A) Positional cloning of the FK gene. RFLP and CAPS markers used for determining recombination break points and corresponding numbers of recombinant chromosomes are indicated. Genetic distances between markers are indicated in cm. The physical map represented by YAC, BAC and cosmid contigs is diagrammed. (█) Mapped YAC or BAC ends, (○) unmapped ends. The two complementing cosmids (shaded) and the 3.1-kb HindIII fragment corresponding to the FK gene are shown (bottom). (B) Nucleotide sequence of the FK gene and deduced amino acid sequence of the encoded protein. Nucleotides in exons are shown in uppercase letters with single-letter amino acid codes below each codon, nucleotides of introns and 5′ and 3′ untranscribed and spliced regions in lowercase letters. Putative GC rich, CAAT and TATA (TAATTTT) boxes in the promoter of FK are underlined. A putative upstream open reading frame (uORF) of six amino acids is boxed. Exons are numbered at their 5′ ends. For exon 1, the inferred 5′ end is the start of the longest 5′ RACE product sequenced. The translation initiation ATG and termination TAG codons are boxed. A putative poly(A) signal (AATAA) is underlined. Mutations identified in the genomic DNAs of fk alleles are marked (*) followed by the allele designation above the DNA sequence.