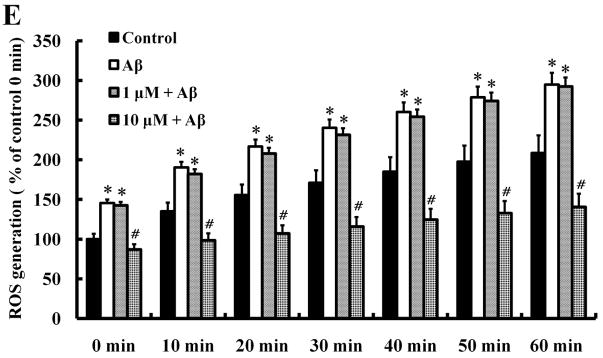
Fig. 3.
Protective effects of morin against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and tau hyperphosphorylation in human neuroblastoma cells.
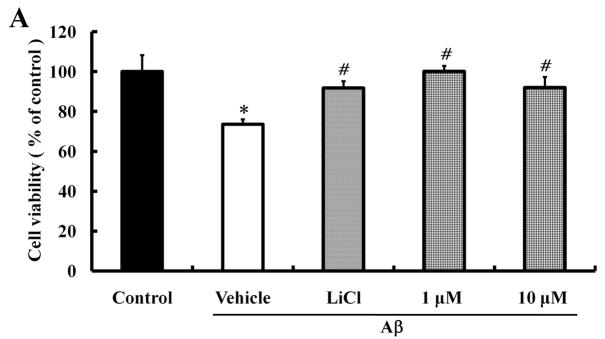
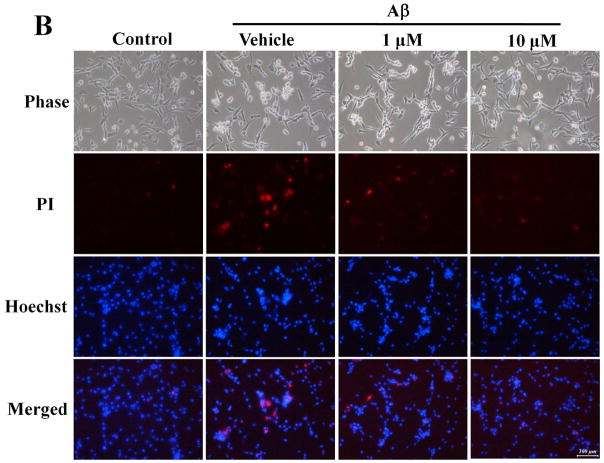
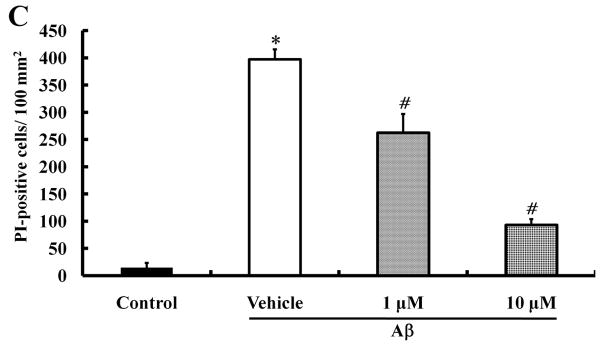
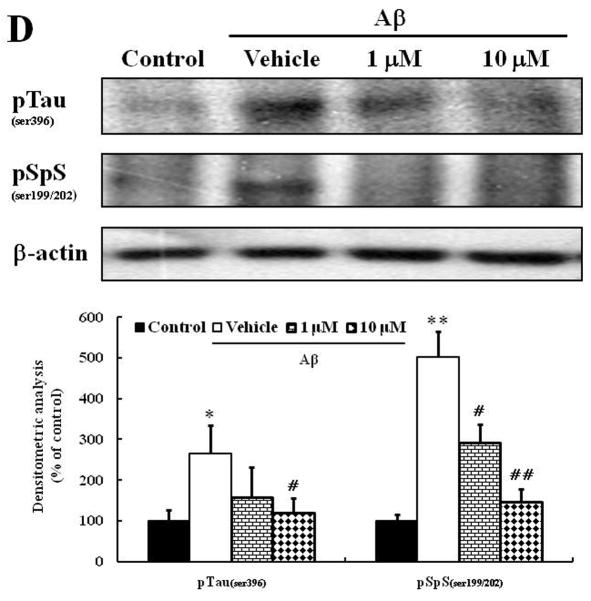
We investigated whether morin prevents Aβ-induced cell death and tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. (A) Cells were pretreated with morin (1 μM or 10 μM) and LiCl (100 μM) for 6 hours, followed by incubation with 10 μM Aβ for 24 hours. Cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. Pretreatment with morin and LiCl significantly increased cell viability in Aβ-treated cells. (B) We confirmed that morin protected against Aβ-induced cell death using Hoechst 33342 and PI staining. (C) Quantitative analysis of the number of PI-stained SH-SY5Y cells. The values are reported as the mean ± S.E.M (n=4). *p<0.01 compared to control. #p<0.01 compared to Aβ-treated culture. Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Whole cell extracts from cells pretreated with morin for 6 hours, followed by treatment with 10 μM Aβ for 24 hours, were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against phosphorylated tau protein (pTauser396, pSpSser199/202). Level of β-actin was used as protein loading control. The blots were quantified by the densitometric analysis. (E) Total ROS were evaluated by DCF-DA method. Exposure to Aβ (10 μM) elevated ROS levels in the cells and morin treatment resulted in a significant attenuation of Aβ-induced ROS production. Values are the mean ± S.E.M (n=8). * p<0.01 compared to control. # p<0.01 compared to Aβ-treated culture (ANOVA with Fisher’s PLSD procedure).