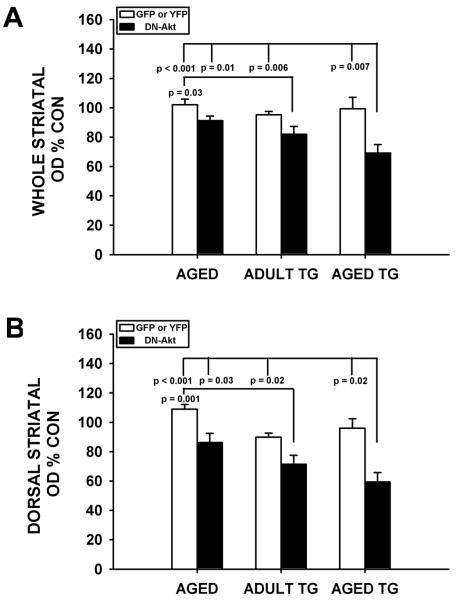
Fig. 5.
Comparison of the effects of age, α-synuclein overexpression and the two factors combined on striatal TH immunoperoxidase staining. A: Each bar represents whole striatal TH optical density on the side of AAV injection as a percent of the optical density on the contralateral non-injected control. The white bars represent the AAV GFP or YFP conditions for each of the three separate experiments, and these values are all close to 100%, as expected. The black bars in each of the three experiments represent the AAV DN(PH)-Akt condition. A significant effect of DN(PH)-Akt to decrease optical density is observed (p < 0.001, ANOVA; Tukey post hoc analysis as shown). In the post-hoc analysis of this comparison, while age alone shows a trend for an effect (an 11% decrease), it does not achieve significance in comparison to any control AAV condition. Transgenic α-synuclein overexpression alone shows a greater effect (a 14% decrease) that is significant in comparison to the AAV GFP condition in the experiment with aged mice (p = 0.03). The two factors combined show a 2-fold larger effect than either single factor alone (a 30% decrease), and this effect is significant in comparison to all AAV control injections. B: An analysis applied to the dorsal striatum alone yields similar results. While age and transgenic α-synuclein overexpression alone both show effects on staining density (by 21% in both cases), the effect of the two factors combined was greater by almost 2-fold (a 38% decrease) (p < 0.001, ANOVA; Tukey post hoc analysis as shown).