Figure 4.
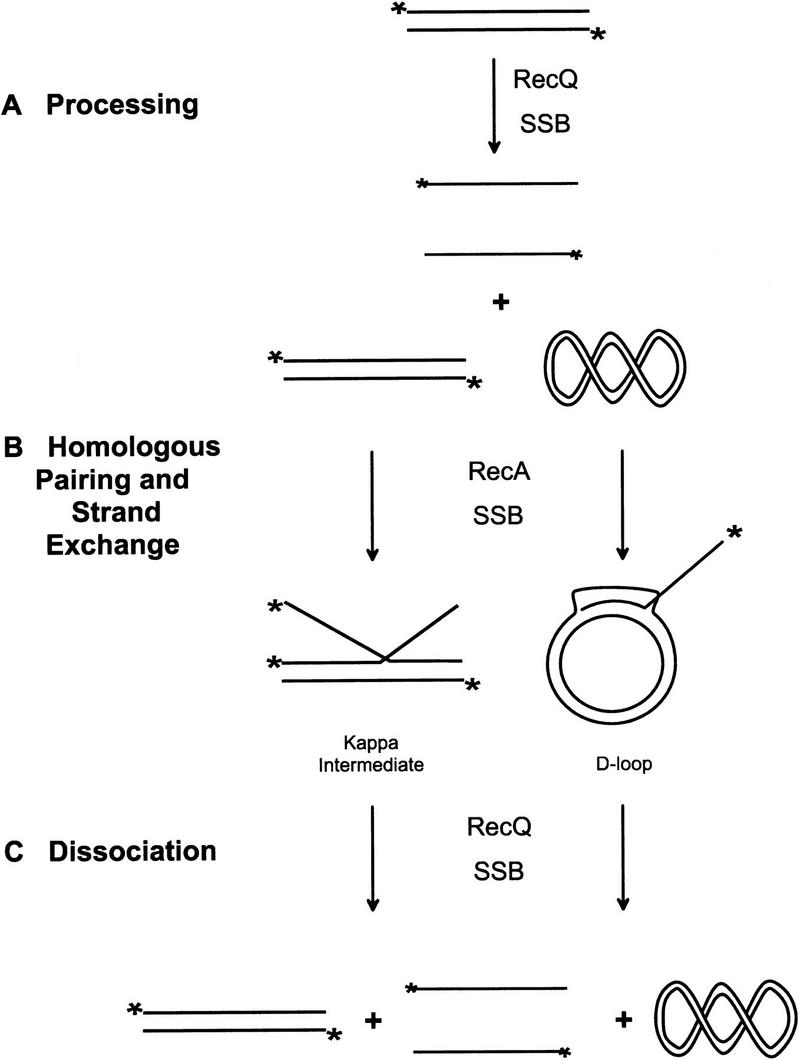
Model for RecQ helicase action in homologous recombination. (A) RecQ helicase initially bound to the 5′-end labeled linear dsDNA substrate unwinds these molecules to produce linear ssDNA. During the unwinding process, SSB protein binds to the liberated ssDNA, trapping it and, thereby, preventing the strands from reannealing. (B) This SSB protein-coated ssDNA is then bound by RecA protein to form a nucleoprotein filament competent for homologous pairing. The RecA nucleoprotein filament initiates homologous pairing and strand invasion to form joint molecules. The major species of joint molecules formed in these reactions are scDNA-dependent D-loops and linear scDNA-independent Kappa intermediates. (C) After the initial unwinding of linear dsDNA, RecQ helicase is available to bind to and dissociate the accumulated joint molecules.
