Figure 4. SK2 channels modulate NMDA receptor-mediated calcium signalling and synaptic plasticity.
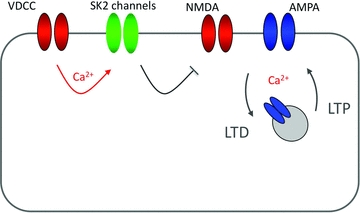
SK2 channels are activated by calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels (VDCCs; P/Q-type channels in cerebellar Purkinje cells). SK conductances reduce calcium influx through NMDA receptor-associated channels, thus influencing the LTD/LTP balance. SK channel blockade thus promotes the induction of LTP in hippocampal pyramidal cells. It is conceivable that in cerebellar Purkinje cells SK channel blockade/amplification of NMDA receptor-mediated calcium transients would facilitate the induction of LTD instead. Calcium sources (VDCCs/NMDA receptors) are shown in red.
