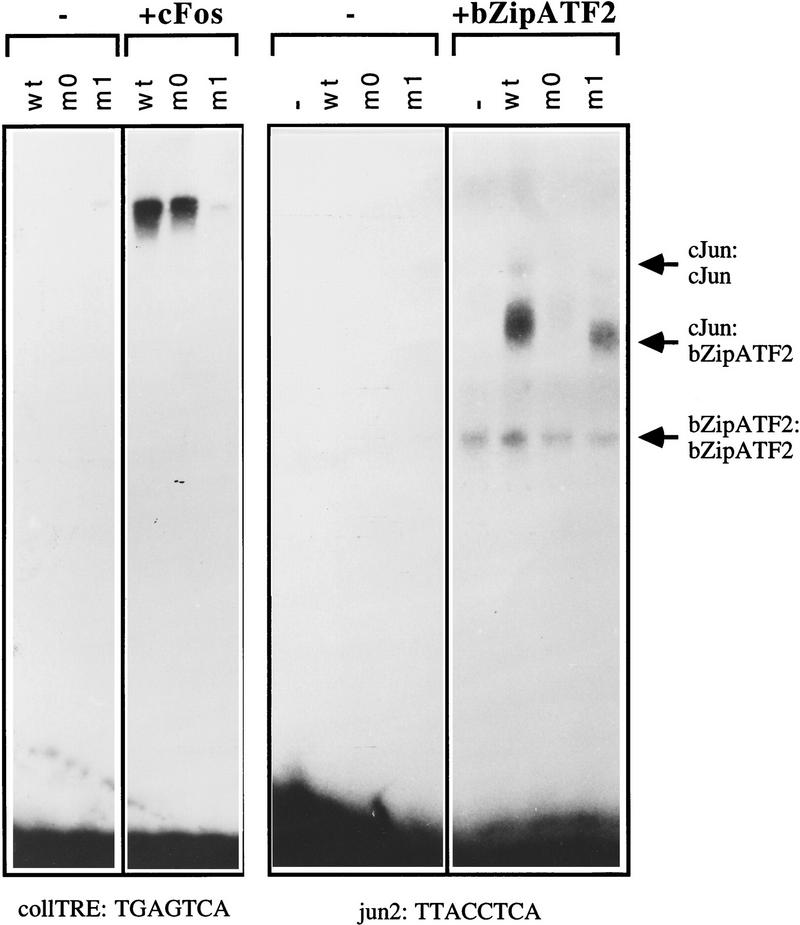
Figure 3.
Dimer-specific DNA-binding properties of c-Jun leucine zipper mutants m0 and m1 in vitro. Gel retardation assays showing the DNA-binding affinities for the collagenase AP-1 binding site (coll–TRE) and the jun2 site of in vitro-translated wild-type and mutant c-Jun proteins in the absence or presence of in vitro-translated c-Fos or bZip–ATF2 (amino acids 335–505). c-Jun proteins were quantified by measurement of the amount of incorporated [35S]methionine, and similar amounts were mixed on ice with control reticulocyte lysate (−) or lysates containing c-Fos or bZip–ATF2 after which 32P-labeled DNA probe was added. The DNA–protein complexes were resolved on 4% polyacrylamide gels and visualized by autoradiography. Note that the increased mobility of the c-Jun–m1:ATF2–DNA complex as compared with that of c-Jun wild-type is explained by a higher negative charge of the c-Jun–m1 protein than of wild-type c-Jun, owing to the replacement of two lysines, an arginine, and a glutamine by four glutamic acid residues.