Figure 4.
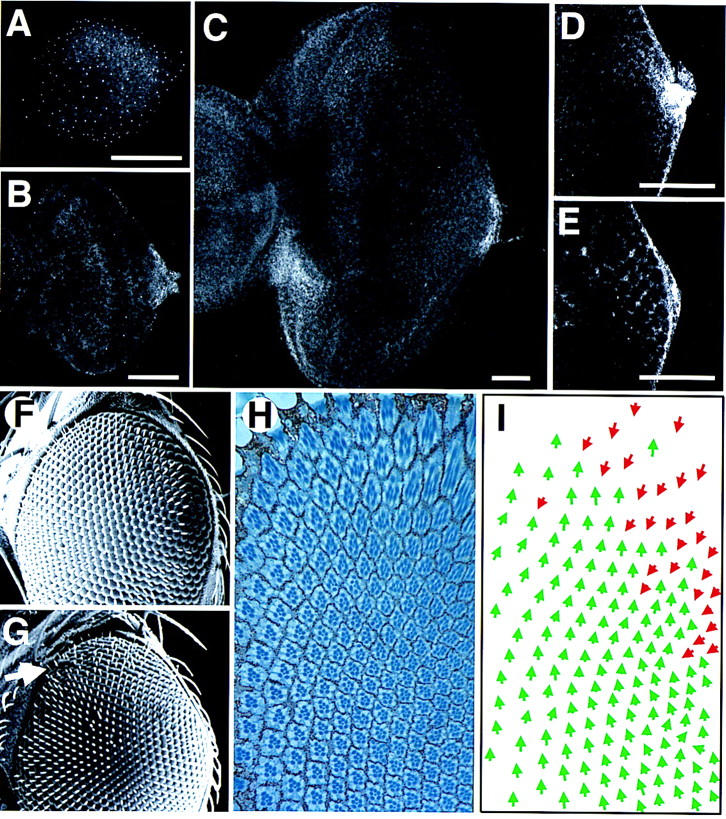
The wild-type expression pattern of Upd and the phenotype induced by ectopic expression of Upd from the poles of the eye. (A–E) The pattern of staining with an anti-Upd polyclonal antibody; scale bars, 50 μm. (A) First instar disc. Staining is faintly visible in a horseshoe around the poles and posterior margin of the disc. The small bright spots of staining distributed across the whole disc may represent staining in the peripodial membrane and/or could be nonspecific. (B) Second instar. Expression is localized to the posterior margin at the DV midline, adjacent to the optic stalk. (C) Late third instar. The furrow has progressed more than halfway across the disc. Expression is still seen localized adjacent to the optic stalk, however, a new region of high-level expression is evident on the ventro–anterior margin adjacent to the antennal disc, which is not present in younger discs (and thus presumably plays no role in ommatidial polarity determination). (D) Higher magnification view of the posterior midline region of an early third instar disc, focused basally. A small cluster of cells shows high-level cytoplasmic expression. (E) More apical view of disc shown in D. A gradient of extracellular Upd can be seen in the extracellular space between the nascent ommatidial clusters. (F) Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of the dorsal half of a wild-type adult eye. (G) SEM of the dorsal half of an eye in which Upd expression was driven at the dorsal and ventral poles during development by the 30A–GAL4 driver at 18°C. The eye appears normal apart from a weak disruption of externally visible facet packing at the dorsal pole (arrow). (H) Section through the dorsal region of an eye similar to G produced by expression of Upd with the 30A–GAL4 driver. The eye is normal in the ventral part of the field (close to the equator), but inverted ommatidia are seen near the dorsal pole. (I) Schematic representation of C. Dorsal ommatidia are shown by green and ventral by red arrows. Note that there is a region of inversion of ommatidial polarity near the dorsal pole, but that ommatidia of both fates are clearly mixed.
