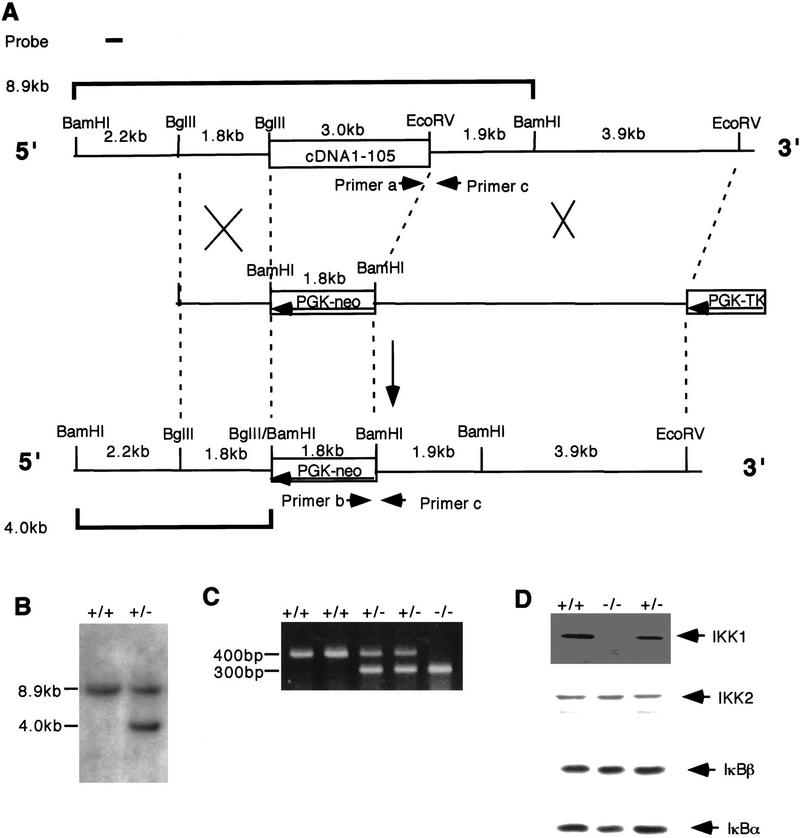
Figure 1.
Targeting of the IKK1 gene in mice. (A) Strategy for targeting the IKK1 allele. Simplified restriction maps of the wild-type IKK1 allele, the targeting construct, and the mutated allele are shown. A 3-kb genomic fragment is deleted and replaced by a PGK–neo cassette in an antisense orientation. (B) Southern blot analysis of an ES clone showing the correct insertion of the targeting construct. DNA was digested with BamHI and hybridized to the probe shown in A. The wild-type allele yields an 8.9-kb fragment whereas the mutant allele yields a 4-kb fragment. (C) PCR detection of mouse genotypes. (D) Western blot analysis confirmed the absence of IKK1 in IKK1−/− MEFs, whereas the expression of IKK2, IκBα, and IκBβ was not changed. Forty micrograms of whole-cell protein lysates from IKK2+/+, IKK2+/−, and IKK2−/− MEFs were loaded and immunoblotted with IKK1, IKK2, IκBα, and IκBβ antibodies.