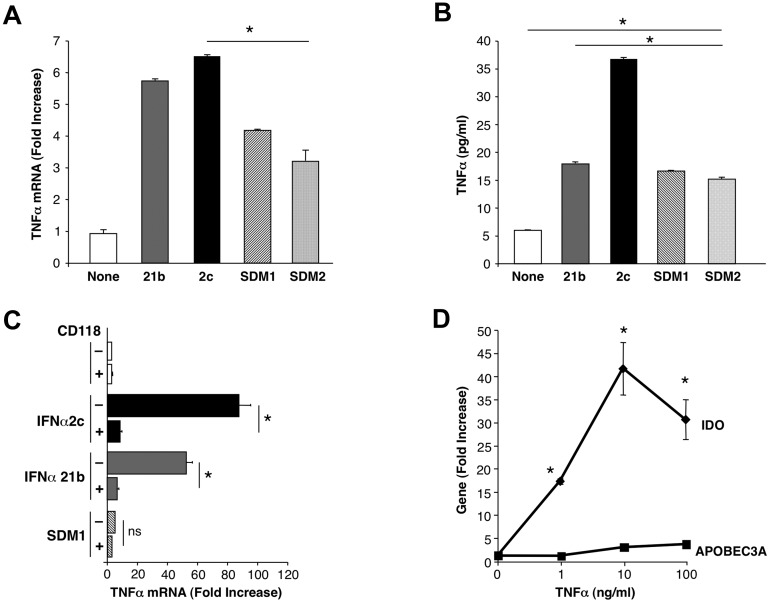
Figure 7.
Differential TNFα induction after exposure to IFN constructs. (A) Macrophages were examined for TNFα gene expression (*P < .003 SDM1 and SDM2 vs IFNα2c; P < .02 SDM1 and SDM2 vs IFNα21b (4 hours) by RT-PCR. P < .002 untreated vs IFN constructs treated macrophages. (B) Supernatant TNFα protein (4 hours) was determined by ELISA (*P < .001 IFN constructs compared with untreated and SDM1 or SDM2 vs parental IFNα2c; mutants vs IFNα21b P < .02). Representative data n = 3. (C) Total mRNA was isolated from macrophages that were incubated with anti-CD118 before treatment with parental IFNs or SDM1 mutant for 4 hours. TNFα gene transcription was examined by RT-PCR. (*P < .01; ns, not significant; P < .01 for parental IFN vs SDM1). (D) Macrophages were treated with rhTNFα (1-100 ng/mL) for 4 hours and total mRNA examined for IDO or APOBEC3A gene expression by RT-PCR. Data represent mean + SEM * P < .05, untreated compared with TNFα-treated.