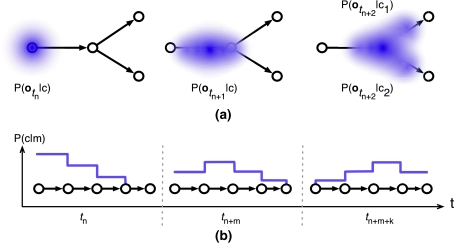
Fig. 4.
a Likelihood of motor command hypotheses at these successive time steps, modeled as four-dimensional Gaussian density functions that change in accord with the motor command. b Likelihood of a motor program hypothesis, modeled as one-dimensional discrete Gaussian density function, stretched over associated motor commands. The density function moves over time along the sequentially connected motor commands