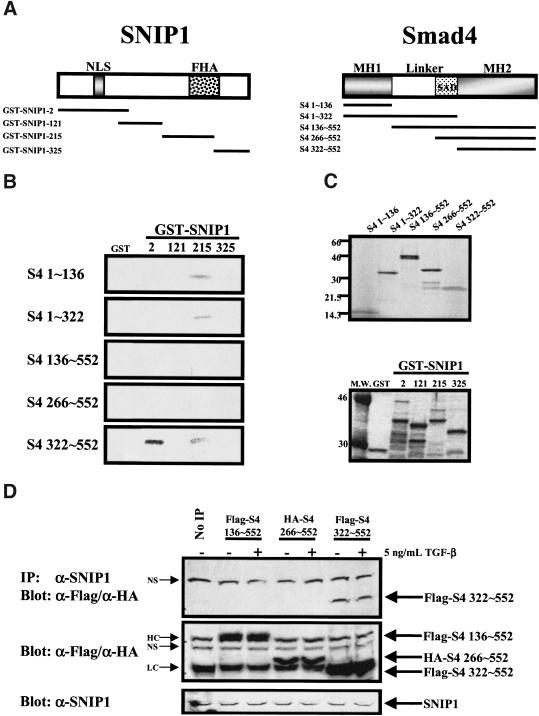
Figure 3.
Deletion mapping of the interacting regions of SNIP1 and Smad4. (A) Schematic diagram of the SNIP1 protein with the GST fusion protein of SNIP1 deletion constructs used in these experiments shown below (left). Numbers indicate the starting amino acid number of the deletion constructs. Smad4 and its deletion constructs used to produce in vitro transcribed/translated products used in the experiment (right). (B) Smad4 deletion constructs from the above diagram were used to make protein using reticulocyte lysate. The Smad4 deletion proteins were used in in vitro-binding assay using various bacterially expressed GST fusion of SNIP1 deletions constructs as indicated. After extensive washing, the beads were subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (C) Twenty-five percent of the reticulocyte lysates used in the reaction was subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiography to monitor for expression of Smad4 constructs (top) GST fusion proteins (25%) were also subjected to standard SDS-PAGE and stained as per experimental protocol to control for equal loading of proteins in the experiments (bottom). (D) NMuMg cell lysates transfected with the indicated deletion constructs Smad4 were treated with or without 5 ng/ml TGF-β for 1 hr. These lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-SNIP1 and blotted with α-Flag and α-HA. No IP lane was immunoprecipitated with rabbit IgG. The presence of SNIP1 in these cells was monitored by direct immunoblotting using antibodies against SNIP1. These lysates were also used for direct immunoblotting with antibodies against Flag and HA to determine the expression of transfected Smad4 deletion constructs. HC and LC denote heavy and light chain of mouse IgG, respectively. (NS) Nonspecific band.