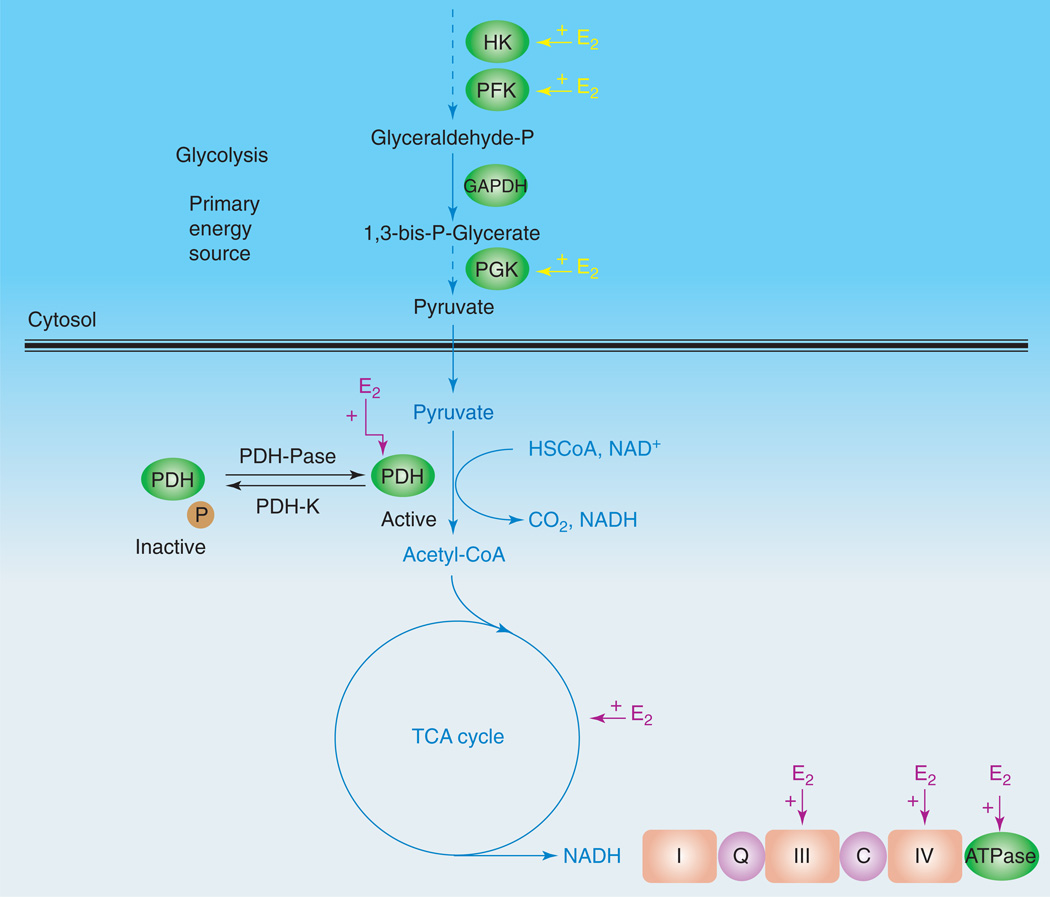
Figure 2.
E2 promotes glycolysis and glycolytic coupled tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) function, mitochondrial respiration and ATP generation. E2 increases key enzymes in the glycolytic pathway to promote the generation of pyruvate and its conversion by PDH to acetyl-CoA to initiate and sustain the TCA cycle. Estrogen enhances glucose uptake into the brain and the glycolytic/pyruvate/acetyl-CoA pathway to generate electrons required for oxidative phosphorylation and ATP generation. Collectively, estrogen enhancement of glucose metabolism and aerobic glycolysis promotes and sustains utilization of glucose as the primary fuel source of the brain, thereby preventing the shift to alternative fuels such as ketone bodies, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease [37]. Abbreviations: C, cytochrome c; HSCoA, coenzyme A; I, complex I of the electron transport chain; III, complex III of the electron transport chain; IV, complex IV of the electron transport chain; PDH-K, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PDH-Pase, pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; Q, coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinol (reduced) or ubiquinone (oxidized).