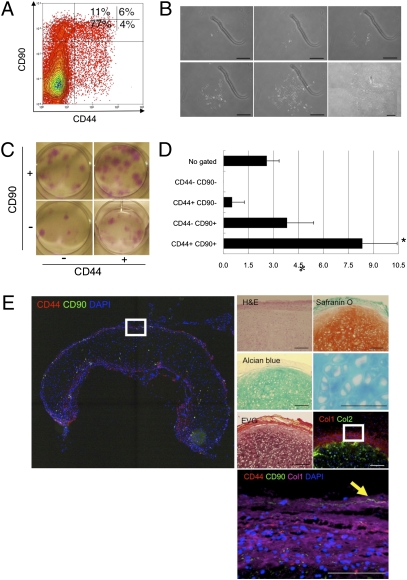
Fig. 5.
Reconstruction of human elastic cartilage by a single CD44+ CD90+ stem cell in the human auricular perichondrium. (A) Perichondrocytes were fractionated via flow cytometry on the basis of the expression of CD44 and CD90. The percentages of each subpopulation are shown. (B) Clonal colony formation of CD44+ CD90+ cells. (The figure is a composite of multiple panels.) (C) Macroscopic observation of clonal colonies derived from multicolor sorted cells visualized using Giemsa staining. (D) Ability of sorted perichondrocytes to form large colonies (LCs). The x axis shows the percentages of cells that formed colonies. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05. (E) Reconstruction of human elastic cartilage by clonally cultured CD44+ CD90+ cells. Reconstructed cartilage consisted of mature chondrocytes with plenty of cartilage ECMs, as evaluated by histochemical staining. The arrowhead shows the retention of a CD44+ CD90+ cell in the reconstructed perichondrium layer. (Scale bars, 100 μm.)