Figure 1.
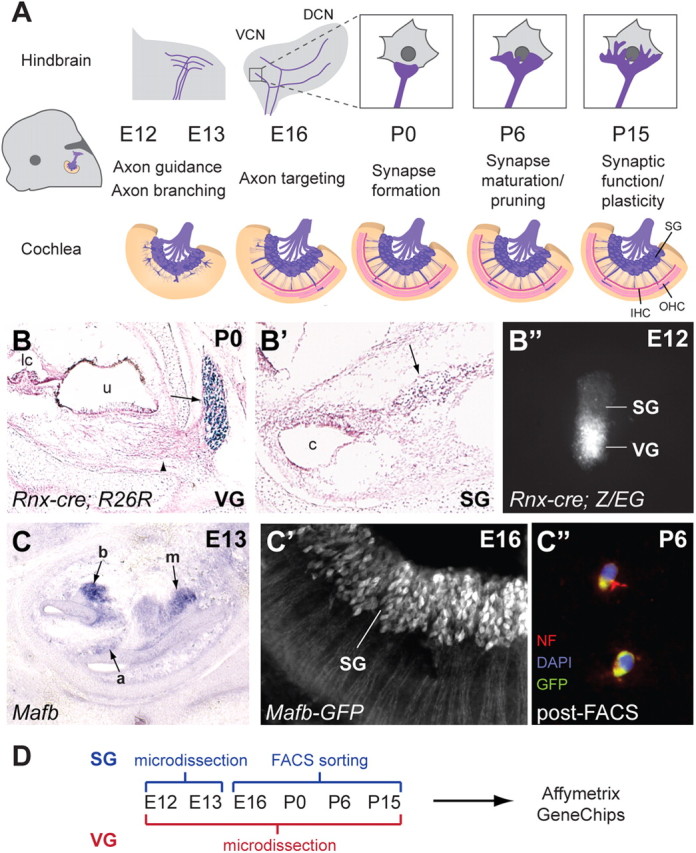
Generation of a gene expression catalog for inner ear neurons during circuit assembly. A, The progression of auditory circuit assembly peripherally (bottom) and centrally (top) from early (E12) to late (P15) time points. At early stages, SG neurons send projections toward the cochlea and hindbrain (axon guidance). The central projection bifurcates to send branches to the DCN and VCN (axon branching). Both peripheral and central projections subsequently find synaptic targets (axon targeting) and form synapses (synapse formation) that mature (synapse maturation/pruning) and become functional (synaptic function/plasticity). IHC, Inner hair cells; OHC, outer hair cells. B–B″, Genetic labeling of the VG using Rnx-Cre. Rnx-Cre drives R26R reporter expression in the VG (arrow in B) but not the SG (arrow in B′), as shown by X-gal staining (blue) at P0 (sections are counterstained with Nuclear Fast Red). Note the peripheral processes extending from the VG toward the utricle (u) (arrowhead in B). lc, Lateral crista; c, cochlea. A microdissected cochlear-vestibular ganglion from an E12 Rnx-Cre;Z/EG embryo shows GFP expression in the VG but not the SG (B″). C–C″, Genetic labeling of the SG using Mafb-GFP mice. Section by in situ hybridization for Mafb at E13 (C) shows strong SG staining in the base of the cochlea (b), weaker staining in the mid-turn (m), and very faint signal in the apex (a). Examination of GFP expression in whole-mount Mafb-GFP cochlea at E16 confirms expression in SG neurons (C′). This expression persists and can be used to isolate SG neurons, as illustrated by immunostaining dissociated P6 Mafb-GFP SG neurons after FACS (C″). The GFP-positive cells (green) also express the neuronal marker Neurofilament (red). DAPI-stained nuclei are in blue. D, A summary of the methods used to isolate SG and VG neurons for Affymetrix Gene Chip analysis at the six chosen stages.
