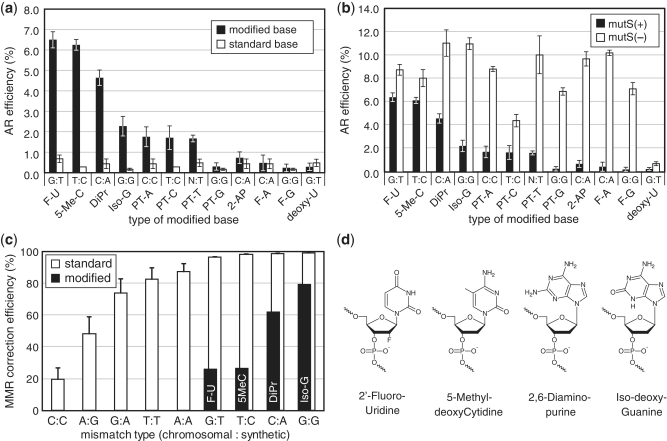
Figure 2.
(a) AR efficiency of oligos with modified bases (black bars) giving rise to different mismatch types [chromosome base : oligo base] and non-modified standard bases (white bars) characterized in a mutS(+) strain (EcNR1). Designation of modified bases are: 2′ Fluoro dU (F-U); 5-Methyl dC (5-Me-C); 2,6-Diaminopurine (DiPr); Iso-dG (Iso-G); Phosphorothioated A (PT-A); Phosphorothioated T (PT-T); Phosphorothioated T (PT-T); Phosphorothioated G (PT-G); Phosphorothioated C (PT-C); 2-Aminopurine (2-AP); 2′ Fluoro dA (F-A); 2′ Fluoro dG (F-G); deoxyUridine. Oligos with Iso-dC and 2′ Fluoro dC had AR efficiency of <0.2%, which was the detectable limit and thus were not shown. The mean and ranges of values are shown for n = 2. (b) AR efficiency of the same oligos with modified bases as in (a), tested in the mutS(+) EcNR1 strain and the mutS(−) EcNR2 strain. The mean and ranges of values are shown for n = 2. (c) White bars correspond to mismatch repair correction efficiency for different mismatch types as computed by difference in AR efficiency in mutS(−) and mutS(+) strains normalized by AR efficiency in mutS(−). Labeled black bars correspond to correction efficiency in oligos with modified bases, showing a drastic decrease compared with standard bases, (G:T with F-U, T:C with 5MeC, C:A with DiPr, G:G with Iso-G). See Table 2 for a list of oligos used. Error bars are standard errors with n = 6–15. (d) Chemical structures of the best-performing modified bases.