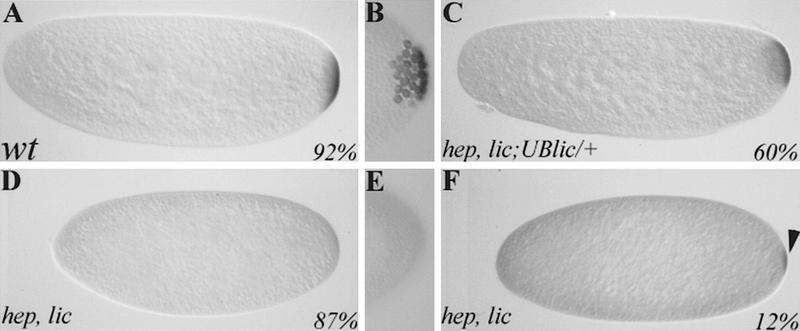
Figure 4.
lic mutations affect pole plasm assembly. Immunostaining of wild-type (A,B), {hep, lic} (D–F), and {hep, lic; UBlic} (C) embryos using an anti-vasa antibody. In wild type, the vasa protein is localized in a posterior crescent in early embryos (A) and becomes incorporated into the pole cells once they form (B). In lic mutant embryos, no (D) or little (F) vasa is present at the posterior pole, and no pole cells form (E). These defects are due to a loss of lic function, as expression of a lic cDNA in the germ line using a UBlic transgene can restore vasa expression and posterior localization (C). Anterior is on the left.