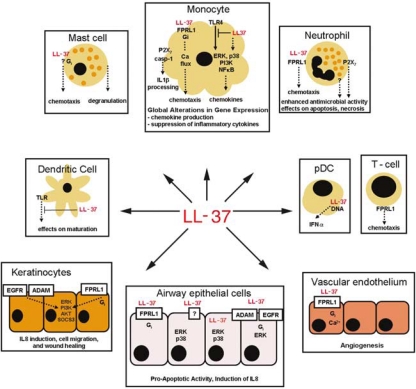
Figure 1.
Immunomodulatory activity of host defence peptides: human cathelicidin LL-37. LL-37 induces global alterations in gene expression in monocytes, signalling through p38, ERK, PI3K, and NF-kB pathways, and promoting expression of chemokines and other genes involved in cell communication and motility.32, (39) LL-37 also acts as a direct chemoattractant for monocytes, neutrophils, T cells, and mast cells through the FPRL1 receptor,35 and an unknown Gi-coupled receptor.36 LL-37 is also strongly anti-endotoxic and inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines in monocytes in response to LPS,40 and also the maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells by TLR ligands.41 In contrast, LL-37 pretreatment of monocytes modulates the process of dendritic cell differentiation, enhancing their function; 42 and in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) LL-37 promotes responses to TLR9 ligands.43 Other activities of LL-37 include the promotion of antimicrobial functions of neutrophils,44 mast cell degranulation,45 and IL-1β processing in LPS-primed monocytes.46 LL-37 also affects neutrophil and epithelial cell apoptosis., 47–49 In keratinocytes, LL-37 induces IL8, and promotes migration and wound healing, and these activities depend on ADAM family metalloproteinase, EGFR and FPRL1.50, (51) In airway epithelial cells, LL-37 activates p38 and ERK pathways and induces chemokine secretion, and this is reported to be mediated by receptors: FPRL1,35, (52) ADAM family metalloproteinase and EGFR,53 and through active peptide internalisation.52 LL-37 also promotes angiogenesis, through FPRL1 receptor on vascular endothelium., 54