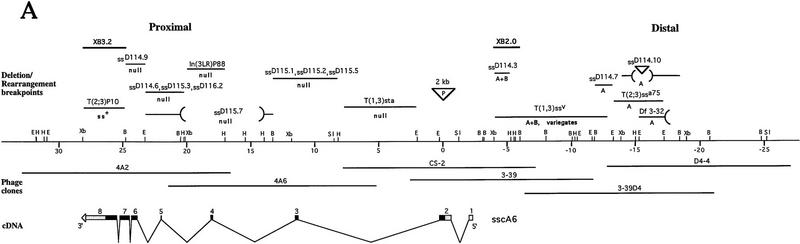
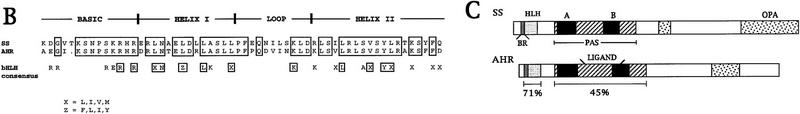
Figure 1.
Molecular analysis of the ss locus. (A) Map of the cloned DNA. Coordinates are in kb; position 0 is the insertion site of the P-element tag used to clone the locus. (B) BamHI; (E) EcoRI; (H) HindIII; (Sl) SalI; (Xb) XbaI. Overlapping phage clones are indicated below the restriction map; phage 3-39 is the P-element containing clone that initiated the walk. The positions of 17 breakpoint mutants are noted above the map; breakpoints and their uncertainties are indicated by lines, deletions by parentheses, and insertions by inverted triangles. The phenotypes of these mutants are noted as null, antennal transformations (A) or antennal transformations coupled with bristle defects (A+B). XB3.2 and XB2.0 indicate genomic fragments that detect transcripts when used to probe Northern blots. Coding sequences and untranslated regions within the exons of the sscA6 cDNA are indicated by black and shaded boxes, respectively. (B) Amino acid identity of ss to AHR in the bHLH domain. Boxed amino acids are identical between the two proteins, and identities of both ss and AHR to the bHLH consensus is noted below. (C) Structure of the ss and AHR proteins drawn to scale. Motifs are noted on the ss protein schematic. (BR) Basic region; (HLH) helix–loop–helix; (A, B, PAS) A and B repeats of the PAS domain; (OPA) region of opa or CAX repeats. The position of the ligand binding domain of AHR is also noted.