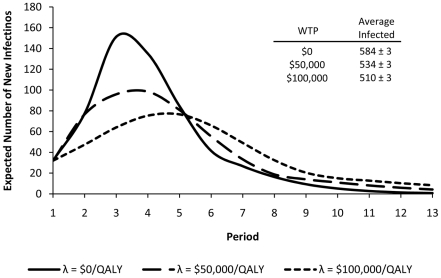
Figure 5. Effect of dynamic health policies on controlling the spread of influenza when no vaccine is available.
As the willingness-to-pay for health increases, the expected number of individuals infected during the epidemic is reduced since the policies corresponding to the higher willingness-to-pay tend to be more aggressive in implementing the transmission-reducing intervention.