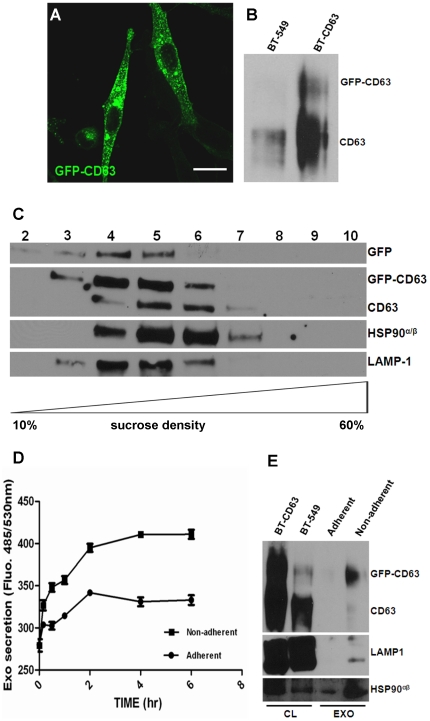
Figure 1. Detection and quantification of intracellular and released exosomes in the conditioned medium of BT-CD63.
(A) BT-549 cells stably expressing GFP-CD63 were grown on glass cover-slips for 24 hours and the intracellular localization of the CD63-associated vesicles visualized by confocal microscopy. Bar is 10 µm. (B) Over-expression of GFP-CD63. Total cell lysates from control BT-549 and BT-549 expressing GFP-CD63 (BT-CD63) cells were analyzed by western blotting and probed with antibodies against CD63. (C) Exosomes purified from the spent media of BT-CD63 cells were layered on top of a sucrose step gradient and centrifuged at 200,000 x g for 4 hours in a Sorvall M150 microcentrifuge. Equal volumes of fractions collected from the top of the gradient (20 µL) were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting for the co-migration of CD63 and the indicated exosomal markers. (D) BT-CD63 cells (5×106) were cultured in complete medium for 24 hours. Adherent cells were maintained in phenol red and exosome-free DMEM/F-12 for the indicated times (0–6 hours). For non-adherent cultures, EDTA-detached cells were resuspended in phenol red and exosome-free DMEM/F-12 for the indicated times (0–6 hours). GFP-CD63 tagged exosomes in the conditioned media were assayed by fluorescence spectroscopy. (E) Purified exosomes secreted for 2 hours from adherent or non-adherent BT-CD63 cells (5×107) were separated in 4-12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and analyzed by western blotting using antibodies against CD63 and the indicated exosomal markers.