Figure 5.
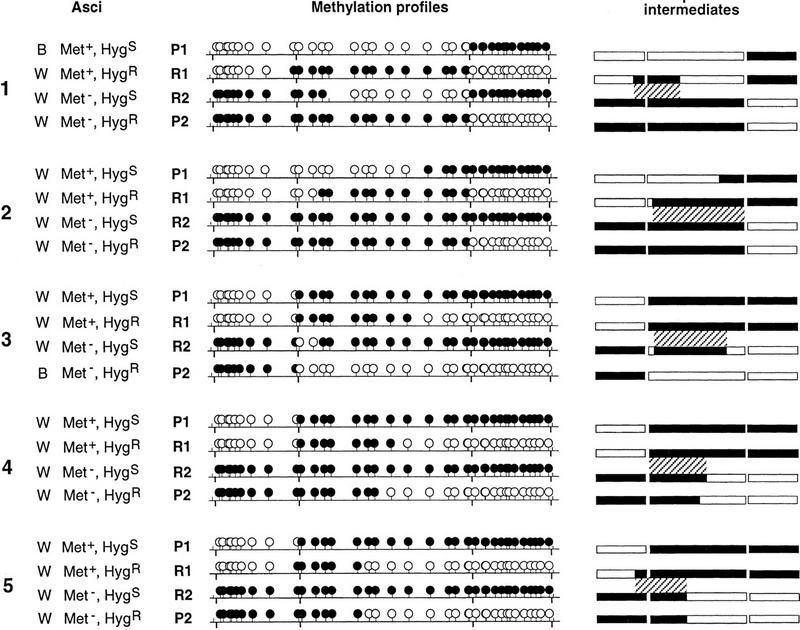
Methylation transfer events associated with crossing-over. The five asci from cross III (asci 1 and 2) and cross IV (asci 3, 4, and 5) showing a crossing-over event (Fig. 2B) are represented (left) with the phenotypes of their four meiotic products. The two parental products are designated P1 and P2; the two recombinant products are designated R1 and R2. The methylation profiles of the four meiotic products of each ascus were determined using the HpaII restriction enzyme. (•) Methylated HpaII sites; (○) unmethylated. The HindIII sites separating the three genes are indicated below the horizontal bar. (Right) Proposed intermediates after methylation transfer. met2, b2, and hph are represented by rectangles; methylated regions are in black and unmethylated regions are in white. For the sake of simplicity, crossing-over was dissociated from transfer of methylation in these drawings. The final products are obtained by performing a reciprocal exchange within the hatched region between the two homologs, which will recombine. This hatched region defines the length of the methylation transfer together with the region where crossing-over must have occurred. Crossing-over outside of this region would have given patched methylation profiles. Methylation transfer involves one (asci 1 and 3) or both (asci 2, 4, and 5) homologous chromatids.
