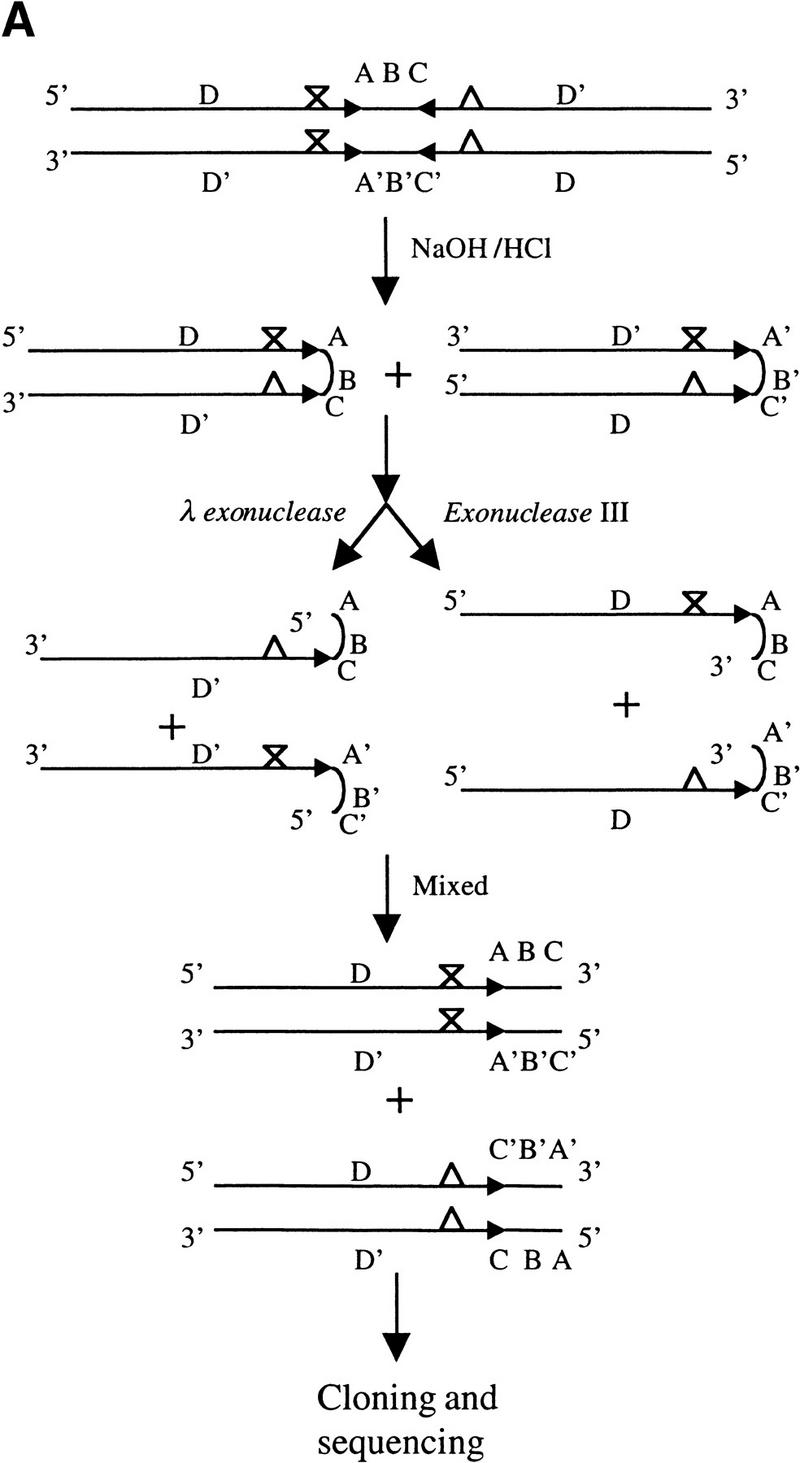
Figure 4.
Strategy for cloning and sequencing long-palindromic DNA and sequencing results. (A) Schematic diagram of a strategy for cloning and sequencing of the junctions of palindromes with adjacent nonpalindromic DNA. DNA fragments containing long palindromes were released from a circular plasmid DNA by restriction enzyme digestion and treated as described in Materials and Methods. X and Δ indicate the position of base-pair differences between the two arms of palindromes. (B) Sequence analysis of the junctions of long palindromes with nonpalindromic DNA. T7 or SP6-specific primers complementary to vector sequences were used. The junctions of long palindromes from pQC143, pQC144, and pQC384 with pSLA2 DNA sequences are shown along with the corresponding segment of the parental pSLA2 plasmid. Short- and long-palindromic sequences are indicated by pairs of arrows. X designates a one base-pair difference between the two arms of a pair of short IRs of pSLA2 that was harmonized in pQC143 and another plasmid, but persistent in the long palindromes of other replicons (data not shown). Pairs of short IRs are numerically designated. Sequences between the limbs of long-palindromes (i.e., spacer regions) of pSLP2-derived plasmids are shown in bold.