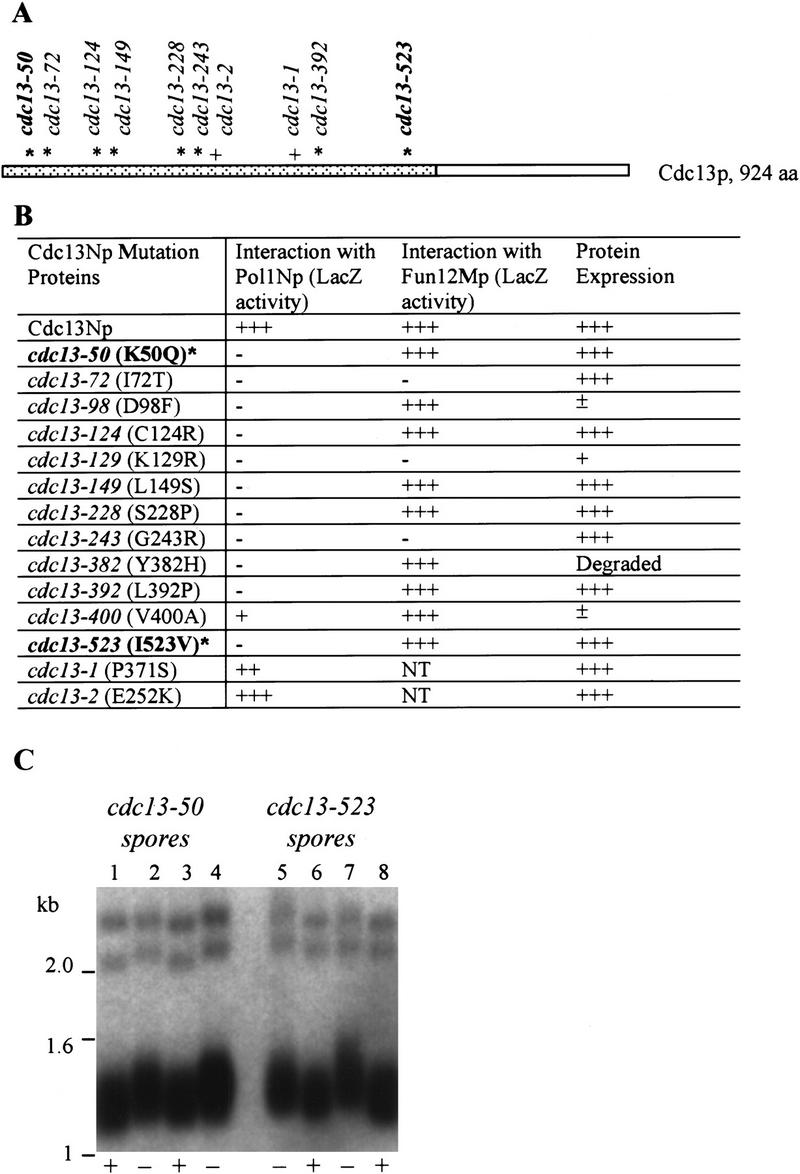
Figure 5.
Alleles of CDC13 that disrupt interactions with POL1. (A) The portion of Cdc13p that was used as bait in the two-hybrid screen is represented by the dotted region. Asterisks mark the sites of single amino acid substitutions that reduced the interaction of Cdc13Np with Pol1Np by two hybrid criteria. The alleles in bold are those used for phenotypic analyses. The locations of the cdc13-1 and cdc13-2 alleles are also indicated (+) (Lin and Zakian 1996; Nugent et al. 1996). (B) Alleles for cdc13 polypeptides that lost interaction with Pol1Np are named by the number of the mutated residue. The amino acid change in each allele is noted in parentheses. Each mutant allele was checked for its ability to interact with both Pol1Np and Fun12Mp in the two hybrid assay using the LacZ filter assay. Western blotting was used to determine if strains carrying the mutant allele made wild-type levels of Cdc13p. (NT) Not tested (+++) wild-type levels of interaction or protein expression, (−) no interaction or protein expression; (±, +, and ++) intermediate levels of interaction or protein expression. (C) XhoI digested DNA from wild-type strain or cdc13Δ strains carrying a centromere plasmid with mutant cdc13 alleles (cdc13-50 and cdc13-523) that disrupted interaction of Cdc13Np with Pol1Np was analyzed by Southern blotting. Only the lower portion of the gels is shown. (+) Wild type (−) mutant cdc13 alleles.