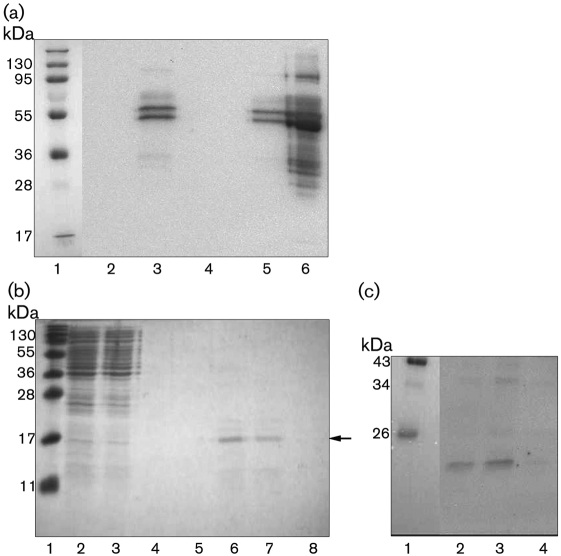
Fig. 4.
Bacteroides bind fibrinogen. (a) B. fragilis and B. thetaiotaomicron were incubated with fibrinogen (300 µg ml−1) or PBS. Bound protein was eluted, analysed by Western blotting and probed with anti-fibrinogen antibodies. Lanes: 1, prestained protein marker; 2, B. fragilis+PBS; 3, B. fragilis+fibrinogen; 4, B. thetaiotaomicron+PBS; 5, B. thetaiotaomicron+fibrinogen; 6, human fibrinogen. (b) Coomassie blue-stained gel showing enrichment of an 18 kDa protein that binds to fibrinogen coupled to Sepharose. Lanes: 1, prestained protein marker; 2, proteins released from the surface of B. fragilis by mutanolysin; 3, run-through from the column; 4–8, protein eluted in fractions from the column. The band indicated with an arrow was subjected to N-terminal amino acid sequencing. (c) Purified proteins from (b) were transferred to a PVDF membrane, incubated with a 20 µg fibrinogen ml−1 solution and probed with an anti-fibrinogen antibody. Lanes: 1, prestained protein marker; 2–4, protein eluted in fractions from the fibrinogen–Sepharose column.