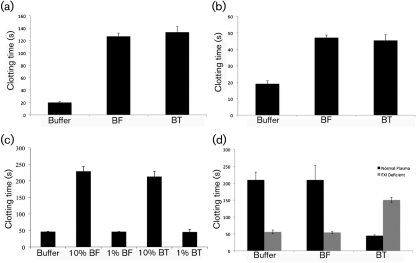
Fig. 5.
Effect of Bacteroides on the intrinsic, extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation. (a–c) B. fragilis (BF) and B. thetaiotaomicron (BT) were incubated with human citrated plasma for 1 h at 37 °C. Bacteria were removed and the resulting plasma supernatants were analysed by clot formation tests. For the negative control, bacteria were substituted with 13 mM sodium citrate solution. Data are means±sd from three experiments. (a) PT clot formation test, (b) TCT clot formation test and (c) aPTT clot formation test. (d) B. fragilis and B. thetaiotaomicron were incubated with human citrated plasma for 1 h at 37 °C. Bacteria were harvested and the resulting plasma supernatants were analysed by the aPTT clot formation test. The resulting bacterial pellets were resuspended in 100 µl FXI-deficient plasma, and clot formation was also analysed. For the negative control, bacteria were substituted with 13 mM sodium citrate buffer. Data are means±sd from three experiments.