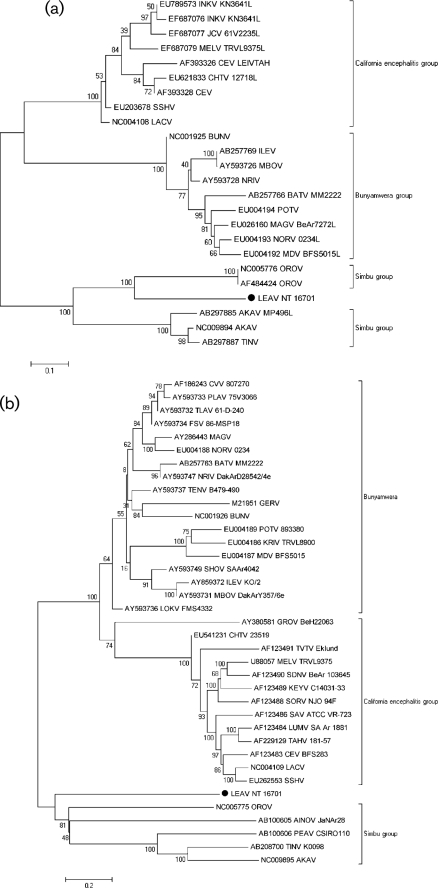
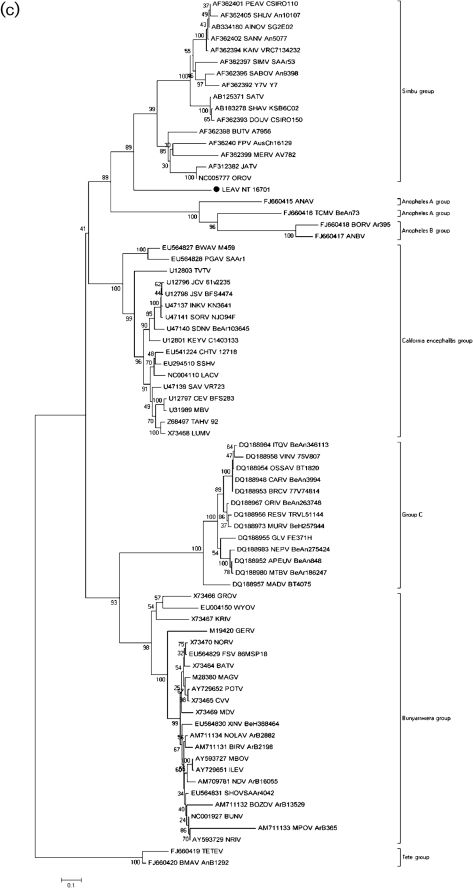
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the (a) polymerase, (b) polyprotein and (c) nucleoprotein of orthobunyaviruses. A set of all complete and partial sequences from GenBank were aligned using the clustal algorithm (as implemented in the mega package version 3) at the amino acid level for the L, M and S segments with additional manual editing to ensure the highest possible quality of alignment. A set of these sequences representing different serogroups were used for analysis, with partial sequences removed for correct tree topology. Neighbour-joining (NJ) analysis at the amino acid level was performed given the high observed variability of the nucleotide sequences. Statistical significance of the tree topology was evaluated by bootstrap resampling of the sequences 1000 times (bootstrap values are shown next to the branches). Phylogenetic analyses were performed using mega software (Kumar et al., 2004). LEAV is marked with a black dot. Bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site.