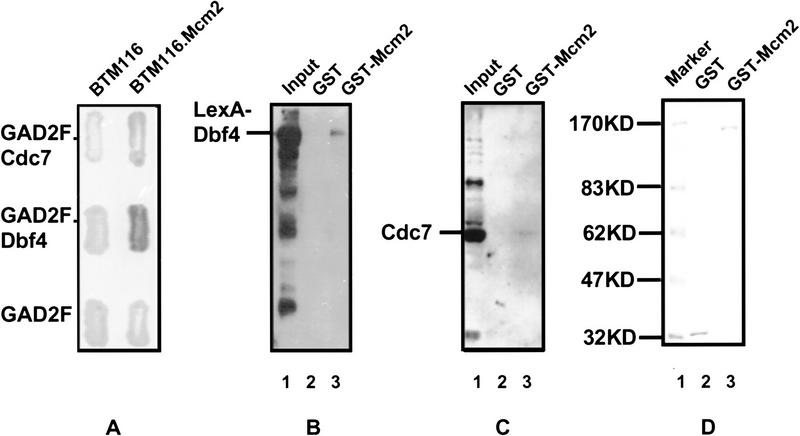
Figure 4.
Physical interactions between Cdc7–Dbf4 and Mcm2. (A) Two-hybrid analysis. BTM116 and BTM116.Mcm2 denote plasmids that express LexA and LexA–Mcm2 proteins, respectively. GAD2F, GAD2F.Cdc7, and GAD2F.Dbf4 denote plasmids that express GAL4, GAL4–Cdc7, and GAL4–Dbf4 proteins, respectively. Yeast transformants carrying each pair of the plasmids and a LexAop–lacZ reporter gene were patched on 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactoside (X-gal) plates. The expression of β-galactosidase is shown by the blue color of colonies. (B,C) GST–Mcm2 fusion affinity column chromatography. (B) Western blot with anti-LexA antibodies. (Lane 1) Total yeast protein extract from BJ2168 cells carrying pKH125; (lane 2,3) proteins eluted from glutathione Sepharose 4B beads coupled with GST (lane 2) and GST.Mcm2 (lane 3). (C) Western blot with anti-Cdc7 antibodies. (Lane 1) Total yeast protein extract from BJ2168 cells; (lanes 2,3) proteins eluted from glutathione Sepharose 4B beads coupled with GST (lane 2) and GST.Mcm2 (lane 3). (D) Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining of a SDS-PAGE showing the GST or GST–Mcm2 released from the beads by 10 mm glutathione after elution of the interacting proteins.