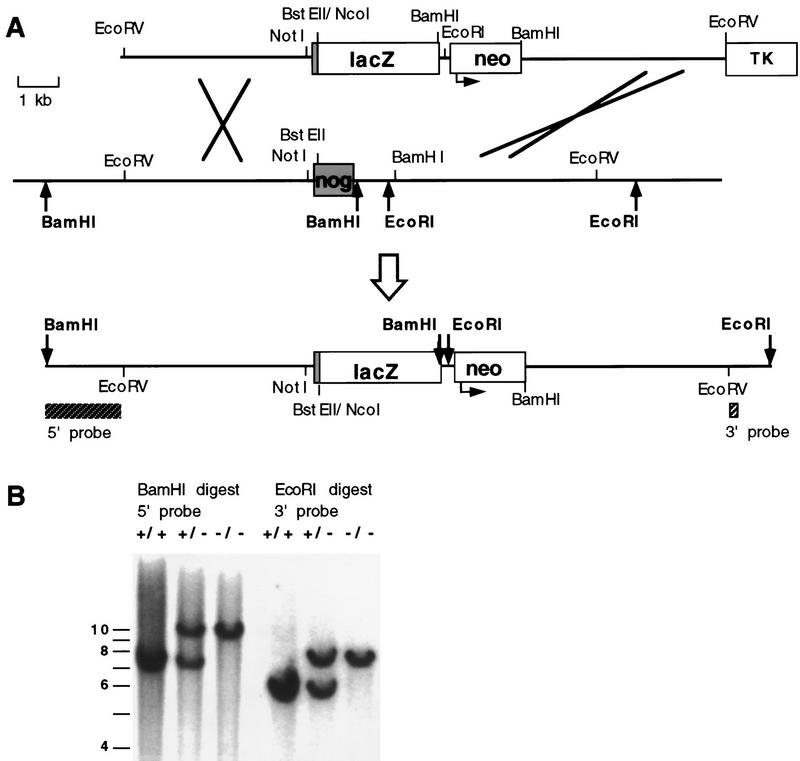
Figure 2.
Gene replacement at the Noggin locus. (A) Schematic representation of gene replacement strategy in which most of the Noggin coding region was replaced by the lacZ gene of E. coli. (Top) Targeting construct that contains 5.2 kb of 5′ flanking sequence with lacZ fused in-frame to the first 10 amino acids of the Noggin coding exon (shaded), followed by a PGKneo cassette (neo; the arrow indicates the direction of transcription from the PGK promoter) and 5.0 kb of 3′ flanking homology starting at the BamHI site, 1.0 kb downstream of the Noggin stop codon. An MC1–HSVTK (TK) cassette was included for negative selection. (Middle) The wild-type Noggin locus with the single Noggin coding exon (shaded). (Bottom) The map represents the expected targeted allele following gene replacement at the Noggin locus. The positions of diagnostic 5′ and 3′ flanking Southern probes are indicated (hatched boxes) and relevant restriction sites used in genotyping are shown in bold. (B) Analysis of Noggin genotypes. Southern blot analysis demonstrating the expected gene replacement at the Noggin locus and germ line transmission of the targeted allele. Homologous recombinants were identified by hybridizing 5′ and 3′ probes external to the targeting vector sequences to genomic DNA digested with BamHI and EcoRI, respectively. The 5′ probe detects a 7.5-kb wild-type and 10.0-kb targeted band and the 3′ probe a 5.8-kb wild-type and 7.5-kb targeted band.