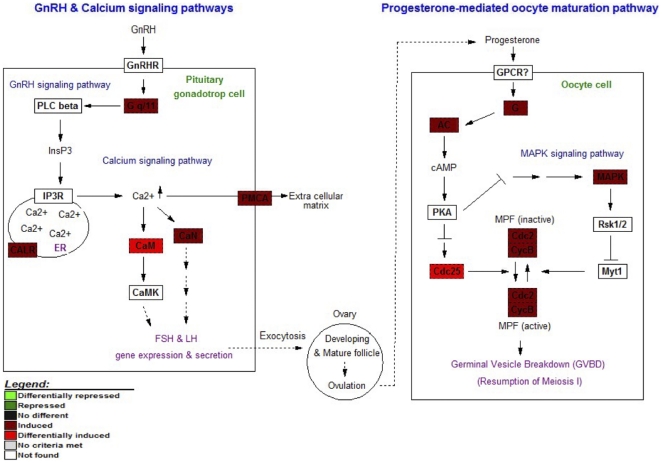
Figure 5. Putative pathways affected by the eyestalk ablation.
The gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation were identified as putative affected pathways containing early induced genes after the eyestalk ablation. The lighter red boxes represent the genes whose expression levels were induced more than 2 fold, whereas the dark red boxes represent the genes whose expression levels were induced less than 2 fold at Day 1 after the ablation. Abbreviation: GnRHR: gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor; G q/11: guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha; PLC beta: phospholipase C beta; InsP3: inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate; IP3R: inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; CALR: calreticulin; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; Ca2+: Calcium ion; CaM: calmodulin; CaMK: calmodulin kinase; CaN: calcineurinB; PMCA: Ca2+ transporting ATPase; GPCR?: G protein-coupled receptor; G: guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha; AC: adenylate cyclase; PKA: cAMP-dependent protein kinase; Cdc25: cell division cycle25; Cdc2: cell division cycle2; CycB: cyclinB; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; Rsk1/2: p90 ribosomal S6 kinase; Myt1: membrane-associated tryrosine and threonine-specific cdc2 inhibitor kinase.