Fig. 1.
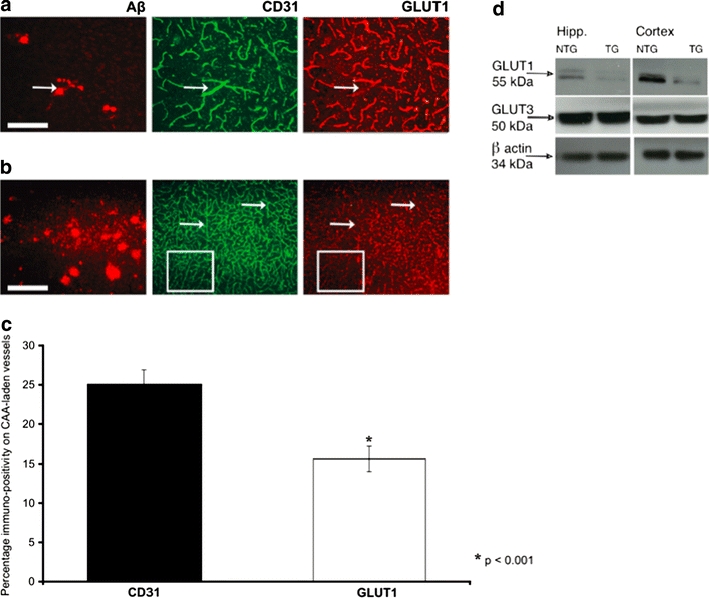
Endothelial GLUT1 but not neuronal GLUT3 protein expression and basal glucose levels are decreased in the TG arcAβ mouse brain from mid-stage pathology onwards. a Immunohistochemical staining of a representative cortical brain section showing GLUT1 protein expression on CAA and non-CAA blood vessels in a mid-stage TG arcAβ mouse. Reduced GLUT1 immuno-staining (arrow) on a CAA-vessel (stained with antibody 6E10, arrow) can be seen. However, CD31—a marker for endothelial cells—was not affected and eventual impaired staining for GLUT1 due to antigen-masking by CAA (arrow) could be ruled out. b Immunohistochemical staining of a representative cortical brain section of a mid-stage arcAβ mouse shows that in areas with dense presence of diffuse Aβ plaques also non-CAA vessels had reduced GLUT1 protein expression, whereas CD31 staining was preserved on these vessels (arrows). CD31 was found to be continuously expressed on the whole length of the vessels in contrast to GLUT1 which showed interruptions in the staining pattern (outlined section). c Statistical analysis of CD31 and GLUT1 expression on CAA-vessels in mid-stage arcAβ mice. Immunostaining for GLUT1 was significantly lower on these CAA-vessels as compared to the CD31 staining. Student’s t test, p = 0.0004 (n = 35 CAA vessels). d Western blots of hippocampus and cortex of mid-stage TG arcAβ mice and NTG littermates demonstrating that the endothelial GLUT1 protein expression (55 kDa) was reduced in TG animals as compared to their NTG littermates. No differences were found in the levels of the neuronal GLUT3 protein. Scale bar a 100 μm; b 300 μm
