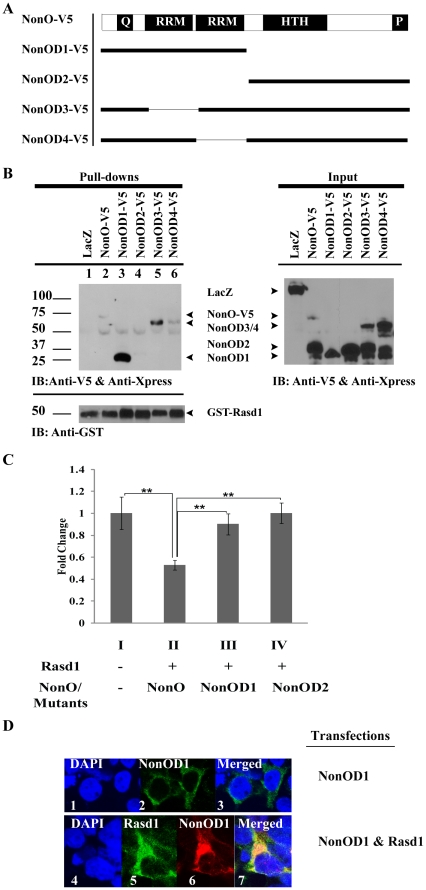
Figure 4. Rasd1 requires full-length NonO to suppress the cAMP pathway in HEK293T cells.
(A) Schematic drawing of the locations of specific domains of NonO protein and its truncated constructs. Q, glutamine-rich region; RRM, RNA-recognition motif; HTH, helix-turn-helix and highly-charged region; P, proline-rich region. Bipartite NLS is located within HTH. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with pGST-Rasd1 along with various constructs of NonO-V5. Lysates were then incubated with MagneGST™ particles, which enable binding of GST-Rasd1. Only NonOD2-V5 did not interact with GST-Rasd1 (Lane 4). Anti-V5 and Anti-Xpress were used for detection of LacZ and all truncated clones of NonO; anti-GST was used for detection of GST-Rasd1. (C) Rasd1 (2 µg) was co-transfected with either NonO or NonO mutants (2 µg) and luciferase assay was performed subsequently. Neither mutant was able to repress CREB's activity in the presence of Rasd1 unlike that of wild-type NonO (compare Histograms II with III and IV). (D) Immunofluorescence studies of NonOD1 and Rasd1 in HEK293T cells. GST-NonOD1 is primarily localised in the cytoplasm (Figure D2). In the event of co-transfection with GST-NonOD1, His-Rasd1 is localised in the cytoplasm, whereas the sub-cellular distribution of His-Rasd1 was concentrated in the nucleus in the presence of NonO (compare Figure 3 A8 with Figure 4 D5).