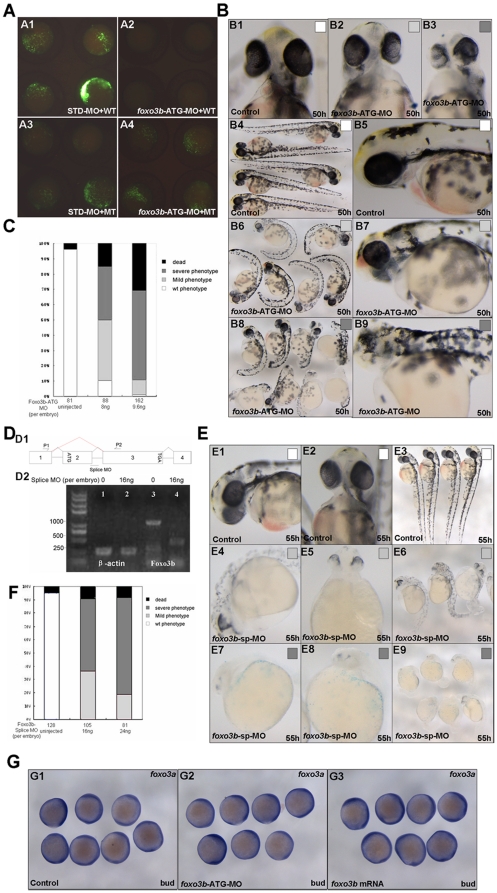
Figure 2. Knockdown of foxo3b results in defects in body axis and brain.
(A) Validation of foxo3b ATG-blocking morpholino (foxo3b-ATG-MO). A1, embryos were injected with STD-MO (8 ng per embryo, control) and a wild-type foxo3b-GFP fusion protein expression vector (WT) and then examined by fluorescence microscopy; A2, embryos were injected with foxo3b-ATG-MO (8 ng per embryo) and a wild-type foxo3b-GFP fusion protein expression vector (WT); A3, embryos were injected with STD-MO and a mutated foxo3b-GFP fusion protein expression vector (MT); A4, embryos were injected with foxo3b-ATG-MO and a mutated foxo3b-GFP fusion protein expression vector (MT). A1-A4, bud stage. (B, C) Morphology of representative morphants in foxo3b-ATG-MO injected embryos. The morphants had shorter body length, abnormal brain and heart at 50 hpf. Black box, dead embryos at 24 hpf; B3, B8, B9, dark gray box, embryos with defects at 50 hpf characterized by severe phenotype: no blood circulation, severely reduced body length and thinner brain; B2, B6, B7, light gray box, embryos with mild phenotype; B1, B4, B5, white box, un-injected wild-type embryos. B1-B3, front views; B4, B6, B8, lateral views; B5, B7, B9, lateral views with anterior to the left. (D) Validation of foxo3b splice-blocking morpholino (foxo3b-SP-MO). D1, Foxo3b exon/intron structure. Foxo3b-SP-MO can alter splicing of foxo3b mRNA, which results in the production of an aberrantly spliced message (as showed by red line). D2, The injection of foxo3b-SP-MO results in the production of a truncated mRNA (440 bp). The embryos were collected at bud stage, and β-actin was used as an internal control. (E, F) Morphology of splice-MO injected embryos. By 55 hpf, the morphants showed defects similar to that of foxo3b-ATG-MO injected embryos. (G) The expression level of foxo3a was not altered in foxo3b-knockdown or foxo3b over-expressed embryos. Embryos were injected with 8 ng foxo3b-ATG-MO (G2) or 1 ng foxo3b mRNA (G3) at 1-cell stage. Wild-type embryos were used as control. G1-G3, bud stage, lateral views.