Figure 1.
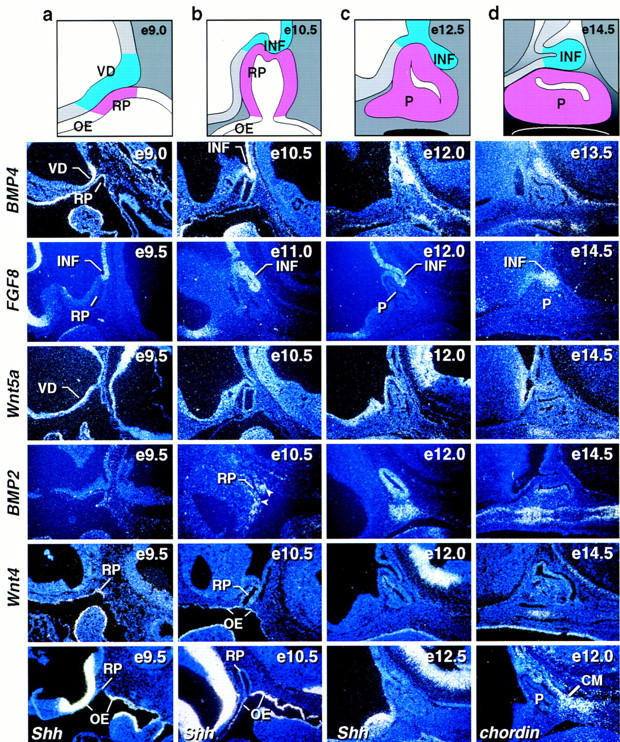
Expression of signaling molecules during early stages of pituitary development. Schematic representation of different stages of pituitary development (a–d). In situ hybridization analysis for BMP4, FGF8, Wnt5a, BMP2, Wnt4, Sonic hedgehog (Shh), and chordin during early stages of pituitary development [embryonic day (e) of mouse development is indicated at top right of each panel]. BMP4 expression is detected early on in the ventral diencephalon and later in the infundibulum to subsequently disappear. FGF8 is expressed temporally later than BMP4 in the infundibulum. Wnt5a is expressed throughout the ventral diencephalon not showing any restriction. No BMP2 expression is detected early in the vicinity of Rathke’s pouch. At E10.5 BMP2 expression was detected in the most ventral part of Rathke’s pouch ectoderm and in some adjacent mesenchymal cells (arrows). By E12.0 BMP2 was expressed throughout Rathke’s pouch and in the underlying condensing mesenchymal cells. Two days later BMP2 expression is confined to the perilumenal cells in Rathke’s pouch and the underlying cartilage growth zone. Wnt4 expression is observed in the oral ectoderm and Rathke’s pouch throughout pituitary gland development. Shh expression is observed throughout the oral ectoderm, whereas the invaginating part of oral ectoderm that becomes Rathke’s pouch is void of any detectable expression, creating a molecular boundary between two ectodermal domains of Shh expressing and nonexpressing cells. The BMP antagonist chordin is expressed in the caudal mesenchyme (CM) adjacent to Rathke’s pouch. BMP2 and Wnt4 expression is noted in the condensing mesenchyme beginning at E12. (INF) infundibulum; (RP) Rathke’s pouch; (OE) oral ectoderm; (P) pituitary; (VD) ventral diencephalon.
