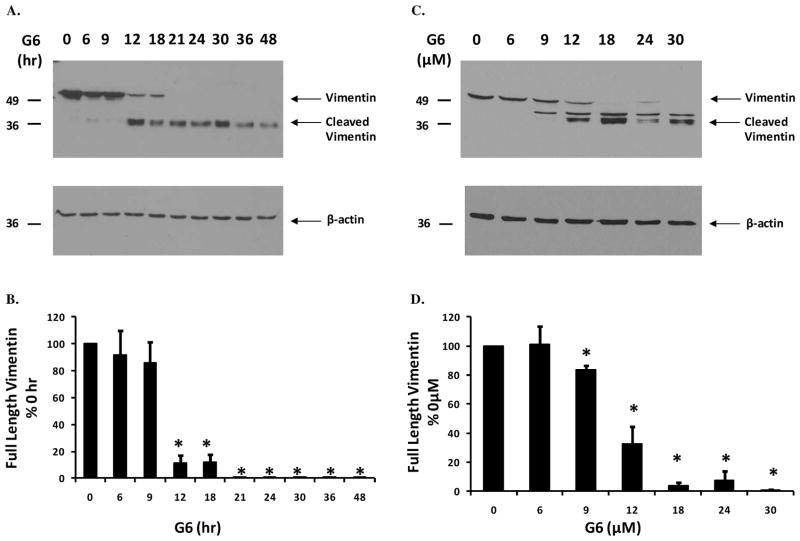
Figure 2. G6 treatment induces time- and dose-dependent degradation of vimentin.
HEL cells were treated either with 25 μM of G6 for varying lengths of time (A) or with increasing doses of G6 for 24 hours (C). Cell lysates were then separated on SDS-PAGE and immunoblottted with an anti-vimentin antibody. The same samples were then reprobed with an anti-β-actin antibody to confirm equal protein loading and also to demonstrate the specificity of G6 for vimentin over other cytoskeletal proteins such as β-actin. Shown is one of three independent results for each. Expression of full-length vimentin was quantified using densitometry and plotted as a function of either time (B) or dose (D) of G6 treatment. Data shown are the mean ± SE from three independent experiments. *p<0.05 with respect to 0 hr (B) or 0 μM (D).