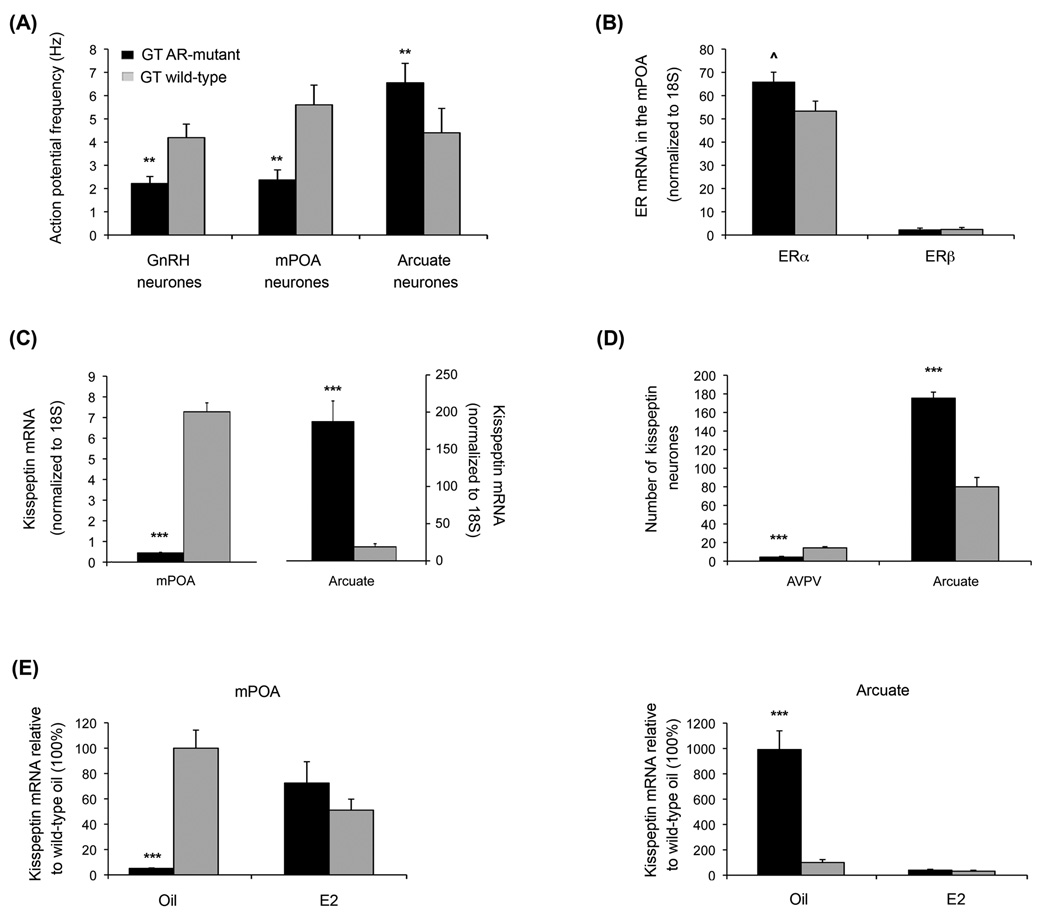
Figure 4.
Characteristics of Neuroendocrine Control Neurones in the GT wild type and GT AR-mutant mouse line. GT AR-mutant and wild type mice were identified by a TaqMan®SNP genotyping assay, which consisted of a common forward and reverse primer and two unique probes based on wild type versus mutant (single base deletion) sequences coupled with different fluorophores (forward primer: 5’-AACTTTCCGCTGGCTCTGT-3’; reverse primer: 5’-CTTGATACGGGCGTGTGGAT-3’; wild type probe: VIC – ACCCCCCGCCCCCT; mutant probe: 6FAM-CACCCCCGCCCCCT). (A) Average AP frequencies recorded in the on-cell configuration from GnRH, mPOA and AVPV neurones. ** Indicates values in wile type male mice were significantly different from AR-mutants with p < 0.01. (B) Relative levels of mRNA encoding ERα and ERβ in mPOA tissue from GT AR mutant and wild type male mice. ^ Indicates a trend that did not attain significance (p = 0.059) towards higher levels of ERα in AR-mutant than wild type male mice. (C) Steady state levels of kisspeptin mRNA were dramatically lower in the mPOA and dramatically elevated in the arcuate of GT AR-mutant versus wild type mice (*** indicates p < 0.001). (D) Immunohistochemical assessment with kisspeptin-10 antibody (Chemicon AB9754, 1:1000) demonstrated significant differences (*** indicates p < 0.001) in the numbers of immunopositive neurones within the 50 µm directly adjacent to the edge of the ventricle in the AVPV and in the arcuate that mirrored differences in mRNA levels for these two regions in GT AR-mutant versus wild type mice. (E) Treatment for two weeks of GT ARmutant male mice with 0.1 mg/kg 17β-oestradiol (E2) restored the pattern of kisspeptin mRNA expression in both the mPOA and the arcuate observed in wild type GT mice.