Figure 4.
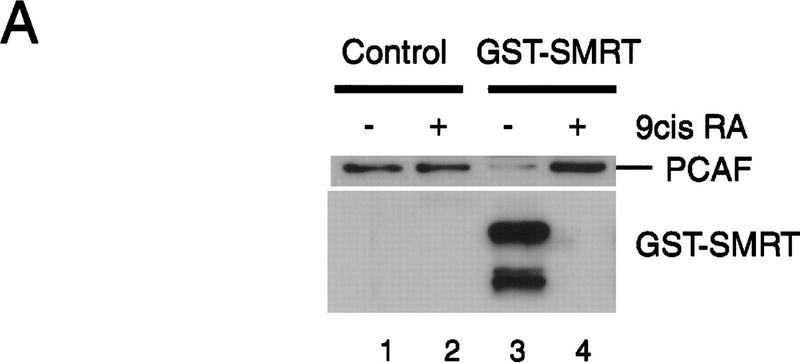
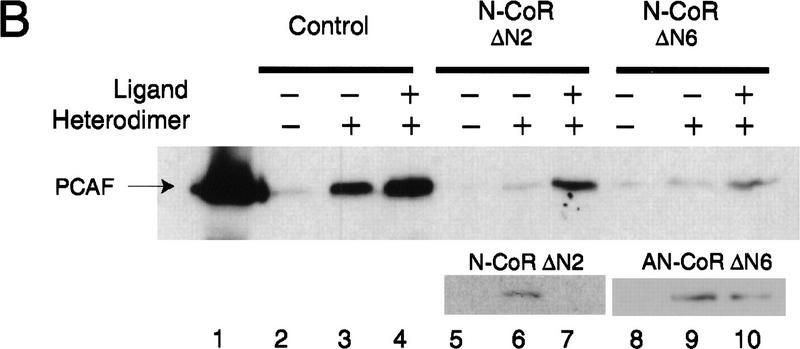
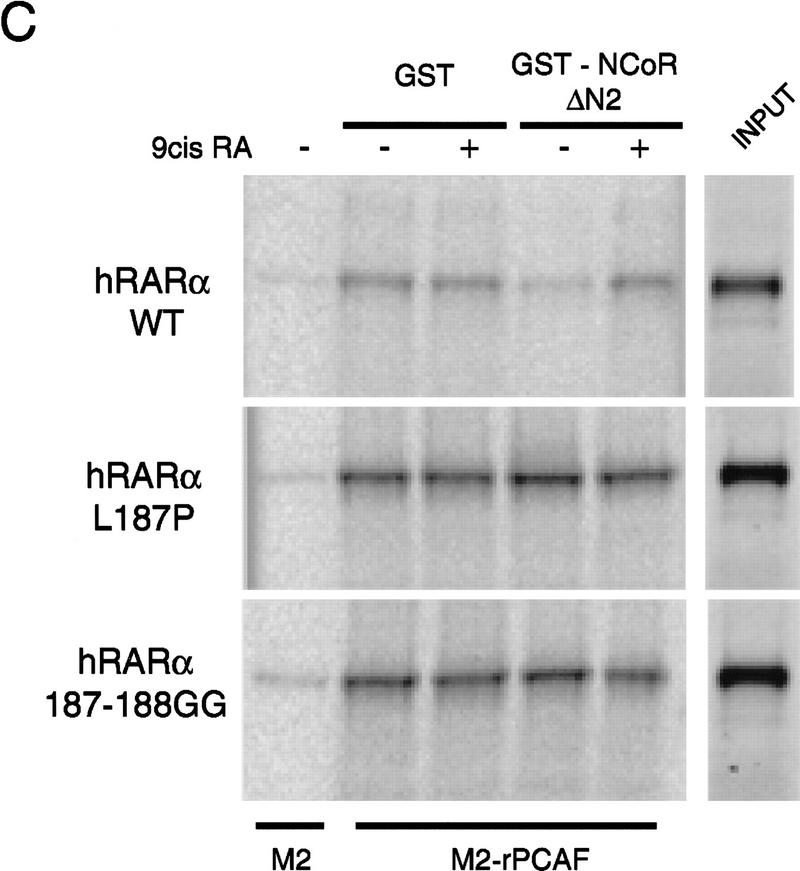
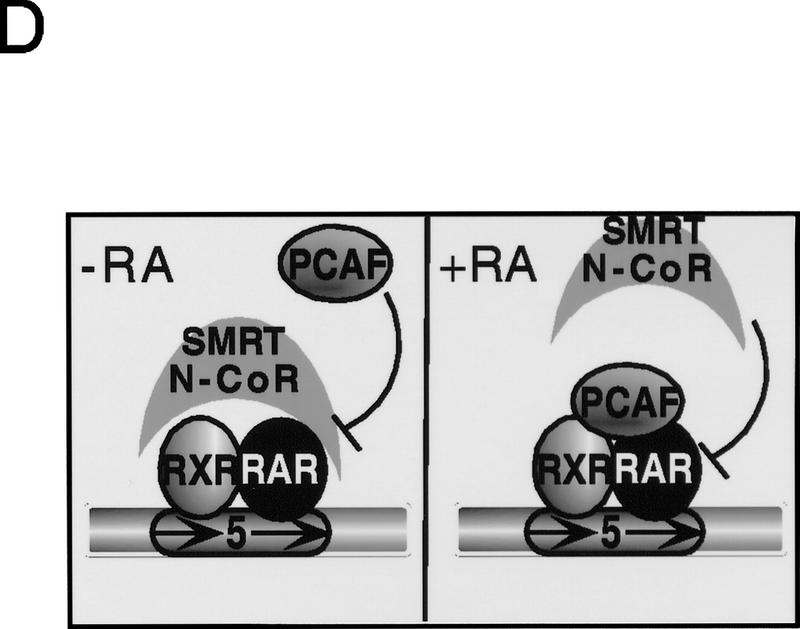
Corepressors enable ligand-dependent binding of PCAF to the RXR–RAR heterodimer in vitro. (A) The effect of SMRT. One microgram of DNA-bound RXR–RAR heterodimers was incubated with 200 ng of rPCAF and 500 ng of control GST (lanes 1,2) or GST–SMRT (lanes 3,4) in the presence or absence of 1 μm 9-cis RA. Binding of PCAF and GST–SMRT to the heterodimer was detected by anti-M2 antibody and anti-SMRT antibody, respectively. (B) The effect of N-CoR. Binding assays were performed as in Fig. 5A, but with 500 ng of control GST (lane 2–4), GST–N-CoRΔN2 (lane 5–7), or GST–N-CoRΔN6 (lane 8–10) with (+) or without (−) 1 μm 9-cis RA. (Bottom) Binding of N-CoR was detected by anti-N-CoR antibody. (C) Ligand-independent PCAF binding to the hinge mutants of RARα. 35S-Labeled, in vitro-translated hRARα wild-type or hinge region mutants (L187P and 187-188GG) (2 × 105 cpm) were incubated with 2 μg of immobilized rPCAF in the presence of GST or GST–N-CoRΔN2 and with (+) or without (−) 1 μm 9-cis RA. (M2) Binding of radiolabeled RARs to the M2 beads without rPCAF; (INPUT) amounts of RARs (2 × 104 cpm) tested in each reaction. (D) Scheme for corepressor dissociation and PCAF binding.