Figure 3.
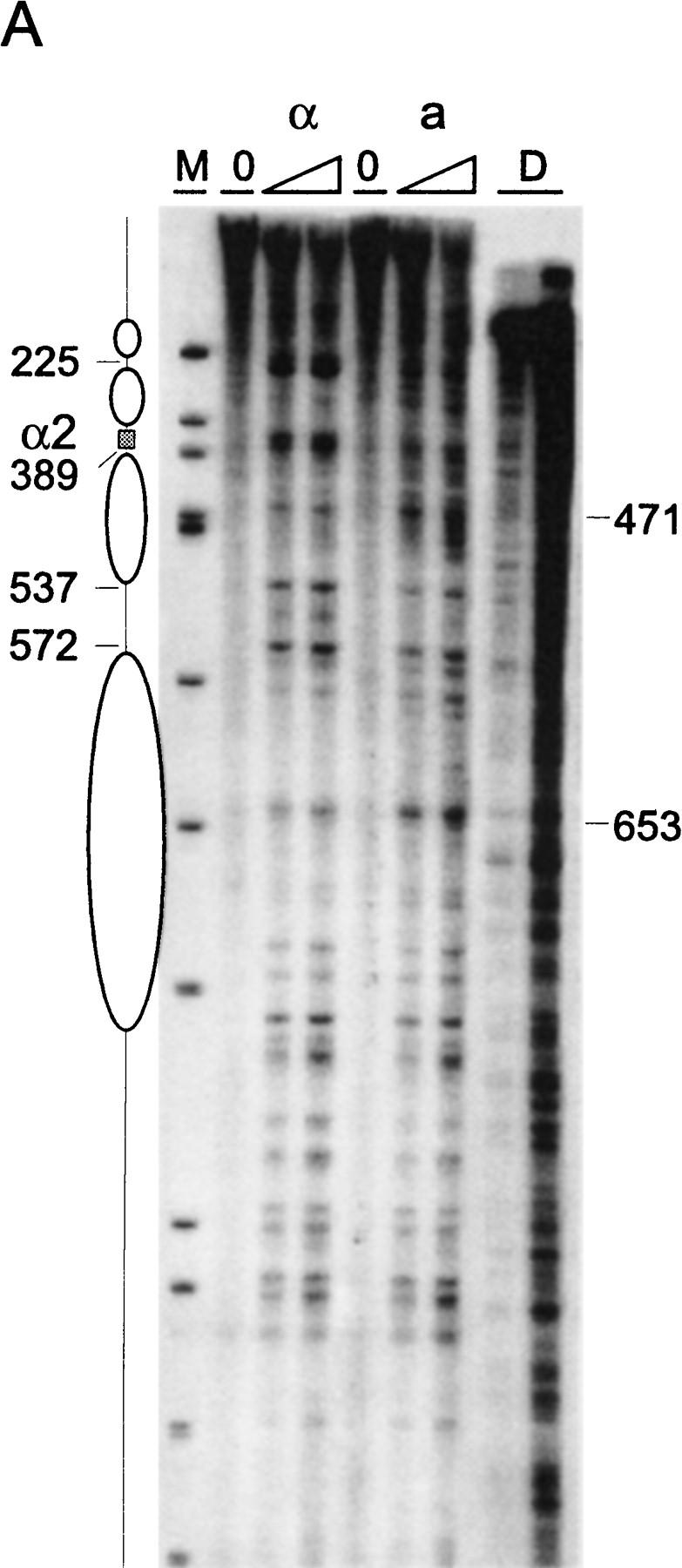
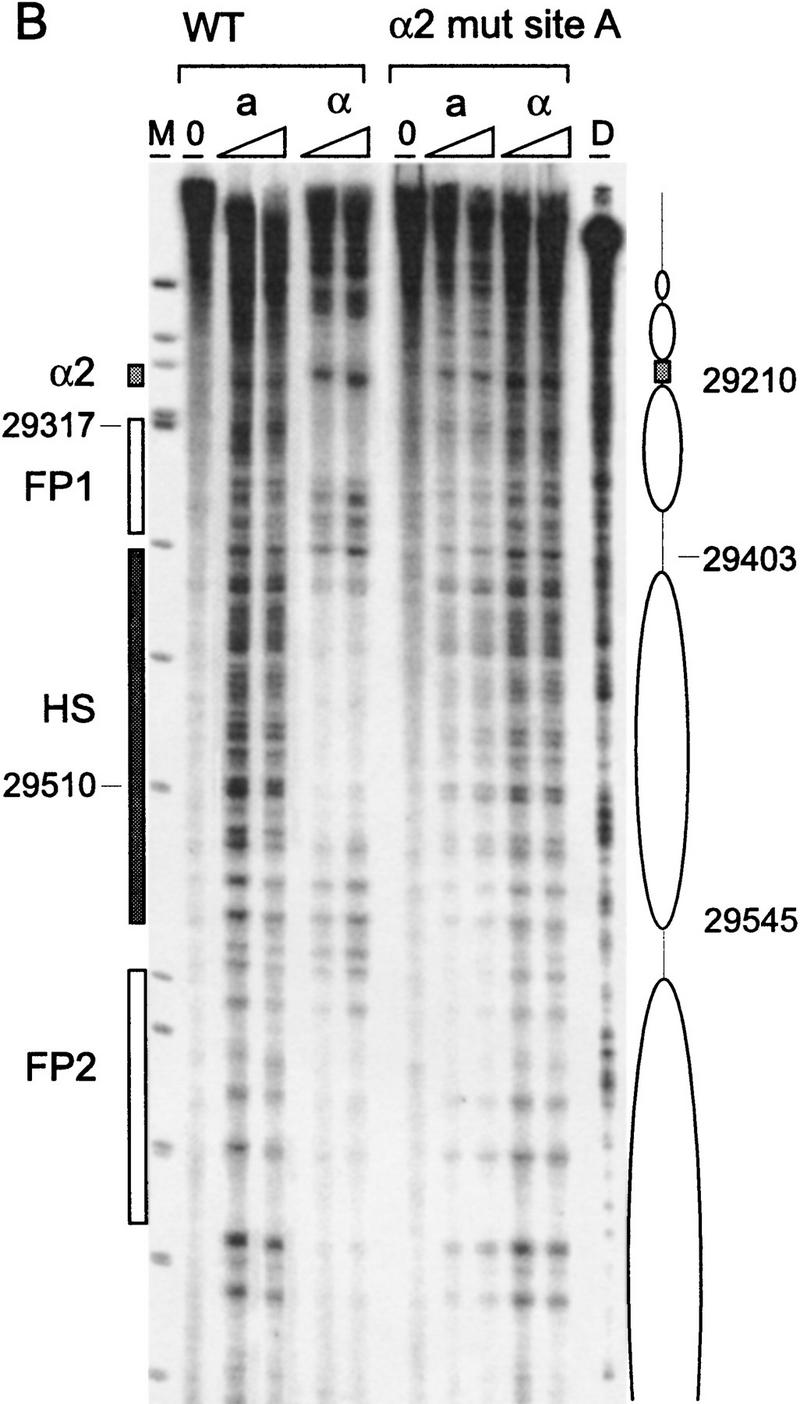
Chromatin structure of REcer and REcarl. (A) Chromatin structure of the S. carlsbergensis 813-bp RE fragment inserted in place of the S. cerevisiae RE at location 28.8 kb of chromosome III. Chromatin structure was mapped by primer extension analysis of micrococcal nuclease cleavage sites with primer I11. MATa and MATα cells are as indicated (CWU61, CWU67). Coordinates correspond to the inserted fragment of REcarl with increasing values for centromere-proximal sequences. Extensions of undigested chromatin (0) and chromatin digested by use of two levels of micrococcal nuclease are presented. (D) Protein-free DNA digests to control for micrococcal nuclease sequence specificity. (M) φX174 DNA digested with HinfII kinased fragments as size standards. The Matα2–Mcm1 binding site (α2) is represented by a shaded box. Inferred positions for nucleosomes in MATα cells are identified by ellipses. (B) Chromatin structure of the wild-type S. cerevisiae 753-bp RE fragment (WT) and the same region containing a 2-bp mutation (GT > G at positions 29198–29199) in Matα2 binding site A. Chromatin structure was mapped by primer extension analysis of micrococcal nuclease cleavage sites with primer b297. MATa and MATα cells (CWU150 and CWU151 for wild type and CWU51 and CWU54 for the Matα2 binding site A mutant) are as indicated. Coordinates correspond to the published sequence of chromosome III (Oliver et al. 1992). Structural elements of the wild-type MATa RE are shown, including two footprints (FP1 and FP2) and a hypersensitive region (HS), both corresponding to DNA regions having numerous repeats of the TTT(A/G) sequence (Weiss and Simpson 1997), are depicted by open boxes. Inferred positions for nucleosomes in wild-type MATα cells are indicated by ellipses.
